Effect of external periodic signals and electromagnetic radiation on autaptic regulation of neuronal firing
- PMID: 33451180
- PMCID: PMC8687208
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-syb.2017.0069
Effect of external periodic signals and electromagnetic radiation on autaptic regulation of neuronal firing
Abstract
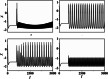
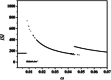
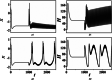
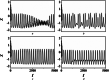
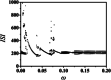
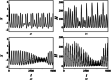
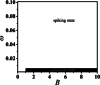
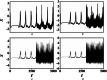
An improved Hindmarsh-Rose (HR) neuron model, where the memristor is a bridge between membrane potential and magnetic flux, can be used to investigate the effect of periodic signals on autaptic regulation of neurons under electromagnetic radiation. Based on the improved HR model driven by periodic high-low-frequency current and electromagnetic radiation, the responses of electrical autaptic regulation with diverse high-low-frequency signals are investigated using bifurcation analysis. It is found that the electrical modes of neurons are determined by the selecting parameters of both periodic high and low-frequency current and electromagnetic radiation, and the Hamiltonian energy depends on the neuronal firing modes. The effects of Gaussian white noise on the membrane potential are discussed using numerical simulations. It is demonstrated that external high-low-frequency stimulus plays a significant role in the autaptic regulation of neural firing mode, and the electrical mode of neurons can be affected by the angular frequency of both high-low-frequency forcing current and electromagnetic radiation. The mechanism of neuronal firing regulated by high-low-frequency signal and electromagnetic radiation discussed here could be applied to research neuronal networks and synchronisation modes.
Keywords: bifurcation; bioelectric potentials; diverse high-low-frequency signals; electrical autaptic regulation; electromagnetic radiation; external high-low-frequency stimulus; external periodic signals; high-low-frequency forcing current; high-low-frequency signal; improved Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model; membrane potential; memristors; neural nets; neuronal firing modes; neurophysiology; numerical analysis; periodic high-low-frequency current; research neuronal networks; synchronisation; synchronisation modes; white noise.
© 2020 The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Figures


References
-
- Izhikevich E.M.: ‘Neural excitability, spiking and bursting’, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos, 2000, 10, pp. 1171–1266
-
- Wig G.S., Schlaggar B.L., and Petersen S.E.: ‘Concepts and principles in the analysis of brain networks’, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2011, 1224, pp. 126–146 - PubMed
-
- Bean B.P.: ‘The action potential in mammalian central neurons’, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2007, 8, pp. 451–465 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

