Observer-based resilient finite-time control of blood gases model during extra-corporeal circulation
- PMID: 33451185
- PMCID: PMC8687436
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-syb.2017.0083
Observer-based resilient finite-time control of blood gases model during extra-corporeal circulation
Abstract
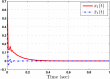
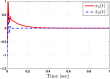
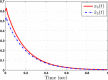
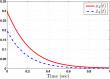
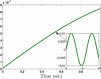
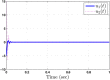
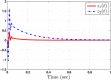
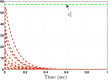
This study aims at designing an observer-based resilient controller to regulate the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood of patients during the extra-corporeal blood circulation process. More precisely, in this study, a suitable observer-based resilient controller is constructed to regulate the levels of patient blood gases in a finite interval of time. The finite-time boundedness with the prescribed performance index of the considered blood gases control system against modelling uncertainty and external disturbances is ensured by using Lyapunov stability analysis. Moreover, a set of sufficient conditions for obtaining the controller gain is developed in the form of linear matrix inequalities (LMIs). Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed robust finite-time control scheme is verified through simulation results. The result reveals that the blood gases are maintained in their physiological ranges during a stable extra-corporeal circulation process via the proposed observer-based resilient controller.
Keywords: CO2; H∞ performance index; LMIs; Lyapunov methods; Lyapunov stability analysis; O2; biomedical equipment; blood; blood gases control system; carbon compounds; carbon dioxide amount; controller gain; controllers; extracorporeal blood circulation process; finite time interval; finite-time boundedness; haemodynamics; linear matrix inequalities; medical control systems; observer-based resilient controller; observer-based resilient finite-time control; oxygen; oxygen amount; patient blood gas levels; physiological ranges.
© 2020 The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Figures
References
-
- Campos F., Sobrino T., and Blanco M. et al.: ‘Glutamate neurotoxicity is involved in the neurological damage in patients undergoing extra‐corporeal circulation’, Int. J. Cardiol., 2014, 172, (2), pp. 481–483 - PubMed
-
- Deng L., Wang B., and Wang Y. et al.: ‘Treatment of bronchial foreign body aspiration with extra‐corporeal life support in a child: a case report and literature review’, Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol., 2017, 94, pp. 82–86 - PubMed
-
- Misgeld B.J.E., Werner J., and Hexamer M.: ‘Robust and self‐tuning blood flow control during extracorporeal circulation in the presence of system parameter uncertainties’, Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 2005, 43, (5), pp. 589–598 - PubMed
-
- Xie A., Yan T.D., and Forrest P.: ‘Recirculation in venovenous extra corporeal membrane oxygenation’, J. Crit. Care, 2016, 36, pp. 107–110 - PubMed
-
- Lim H.S., Howell N., and Ranasinghe A.: ‘Extracorporeal life support: physiological concepts and clinical outcomes’, J. Card. Fail., 2017, 23, (2), pp. 181–196 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

