Survival benefit of ixazomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (IRD) over lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma patients in routine clinical practice
- PMID: 33451293
- PMCID: PMC7810195
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07732-1
Survival benefit of ixazomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (IRD) over lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma patients in routine clinical practice
Abstract
Background: We have performed a head to head comparison of all-oral triplet combination of ixazomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone (IRD) versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (RD) in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) in the routine clinical practice.
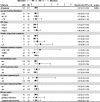
Methods: A total of 344 patients treated with IRD (N = 127) or RD (N = 217) were selected for analysis from the Czech Registry of Monoclonal Gammopathies (RMG). Descriptive statistics were used to assess patient's characteristics associated with the respective therapy. The primary endpoint was progression free survival (PFS), secondary end points included response rates and overall survival (OS). Survival endpoints were plotted using Kaplan-Meier methodology at 95% Greenwood confidence interval. Univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the effect of treatment regimens and the significance of uneven variables. Statistical tests were performed at significance level 0.05.
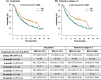
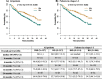
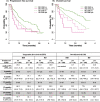
Results: In the whole cohort, median PFS for IRD was 17.5 and for RD was 11.5 months favoring the all-oral triplet, p = 0.005; in patients within relapse 1-3, the median PFS was 23.1 vs 11.6 months, p = 0.001. The hazard ratio for PFS was 0.67 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.51-0.89, p = 0.006). The PFS advantage translated into improved OS for patients treated with IRD, median 36.6 months vs 26.0 months (p = 0.008). The overall response rate (ORR) was 73.0% in the IRD group vs 66.2% in the RD group with a complete response rate (CR) of 11.1% vs 8.8%, and very good partial response (VGPR) 22.2% vs 13.9%, IRD vs RD respectively. The IRD regimen was most beneficial in patients ≤75 years with ISS I, II, and in the first and second relapse. Patients with the presence of extramedullary disease did not benefit from IRD treatment (median PFS 6.5 months). Both regimens were well tolerated, and the incidence of total as well as grade 3/4 toxicities was comparable.
Conclusions: Our analysis confirms the results of the TOURMALINE-MM1 study and shows benefit of all-oral triplet IRD treatment versus RD doublet. It demonstrates that the addition of ixazomib to RD improves key survival endpoints in patients with RRMM in a routine clinical setting.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Dexamethasone; Ixazomib; Lenalidomide; Multiple myeloma; Patient registry.
Conflict of interest statement
JM received honoraria from Amgen, Takeda, Celgene, Janssen, BMS. JR received honoraria from Amgen and MSD. TJ received personal fees from: Amgen, Takeda, Celgene, Janssen, Karyopharm. IS received honoraria from Celgene, Amgen, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, BMS, Novartis, Sanofi, VM had consultancy and received honoraria from Janssen, Amgen, Celgene, Takeda, participated on advisory boards: Janssen, Amgen, Celgene, BMS, Takeda, JS received honoraria from Celgene, Amgen, Takeda, Jannsen, BMS.LC and LB declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Leleu X, Masszi T, Bahlis NJ, et al. Patient-reported health-related quality of life from the phase III TOURMALINE-MM1 study of ixazomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone versus placebo-lenalidomide-dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Am J Hematol. 2018. 10.1002/ajh.25134. - PubMed
-
- Kumar SK, Berdeja JG, Niesvizky R, et al. Safety and tolerability of ixazomib, an oral proteasome inhibitor, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone in patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma: an open-label phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(13):1503–1512. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71125-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

