Combined antegrade femur lengthening and distal deformity correction: a case series
- PMID: 33451359
- PMCID: PMC7809855
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-02168-6
Combined antegrade femur lengthening and distal deformity correction: a case series
Abstract
Background: Leg length discrepancy is often associated with distal femur angular deformities such as valgus or flexion. This study aims to report a new technique for simultaneous limb lengthening and acute distal femoral angular correction.
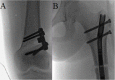
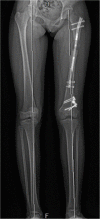
Methods: A retrospective chart review of patients undergoing a single procedure was conducted. Patients included had a single operation where they underwent distal femur osteotomy stabilized with a plate followed by antegrade nailing with a magnetically controlled intramedullary lengthening nail (PRECICE, Ellipse Technologies, Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) using a trochanteric entry.
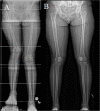
Results: Seven femurs from 7 patients were included. The average age at operation was 13.6 years, and the leg length difference was 51 mm (range 30-105 mm). Associated deformities were valgus (4), knee flexion contracture (2), and both valgus and flexion contracture (1). Lengthening achieved was 43 mm (P = 0.0036), with a consolidation index of 27 days/cm and reliability of 0.87 (6/7). The 5 patients with angulation had an improvement of valgus from 12 to 4° (P = 0.006) and of the mechanical axis deviation from 34 to 3 mm (P = 0.0001). The range of motion also improved in the 3 patients with contractures. Preoperative gait disturbance, hip and knee pain, and functional scoliosis resolved after the limb deformities were corrected.
Conclusion: Combining a magnetic internal lengthening nail with a second distal osteotomy stabilized with a plate can successfully correct limb length and distal femur deformity acutely without altering the expected result of each procedure.
Keywords: Combined femoral deformities; Leg length discrepancy; Limb lengthening; Magnetic intramedullary nailing; PRECICE nail; Two-level osteotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ilizarov GA. The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues: part II. The influence of the rate and frequency of distraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(239):263–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

