Filgotinib in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and limited or no prior exposure to methotrexate: the phase 3, randomised controlled FINCH 3 trial
- PMID: 33452004
- PMCID: PMC8142453
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219213
Filgotinib in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and limited or no prior exposure to methotrexate: the phase 3, randomised controlled FINCH 3 trial
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate efficacy and safety of the Janus kinase-1 inhibitor filgotinib in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with limited or no prior methotrexate (MTX) exposure.
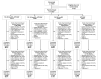
Methods: This 52-week, phase 3, multicentre, double-blind clinical trial (NCT02886728) evaluated once-daily oral filgotinib in 1252 patients with RA randomised 2:1:1:2 to filgotinib 200 mg with MTX (FIL200 +MTX), filgotinib 100 mg with MTX (FIL100 +MTX), filgotinib 200 mg monotherapy (FIL200), or MTX. The primary endpoint was proportion achieving 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20) at week 24.
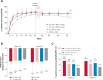
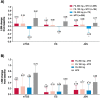
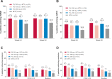
Results: The primary endpoint was achieved by 81% of patients receiving FIL200+ MTX versus 71% receiving MTX (p<0.001). A significantly greater proportion treated with FIL100+ MTX compared with MTX achieved an ACR20 response (80%, p=0.017) at week 24. Significant improvement in Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index was seen at week 24; least-squares mean change from baseline was -1.0 and -0.94 with FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX, respectively, versus -0.81 with MTX (p<0.001, p=0.008, respectively). Significantly higher proportions receiving FIL200+MTX (54%) and FIL100+MTX (43%) achieved DAS28(CRP) <2.6 versus MTX (29%) (p<0.001 for both) at week 24. Hierarchical testing stopped for comparison of ACR20 for FIL200 monotherapy (78%) versus MTX (71%) at week 24 (p=0.058). Adverse event rates through week 52 were comparable between all treatments.
Conclusions: FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX both significantly improved signs and symptoms and physical function in patients with active RA and limited or no prior MTX exposure; FIL200 monotherapy did not have a superior ACR20 response rate versus MTX. Filgotinib was well tolerated, with acceptable safety compared with MTX.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis; rheumatoid; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RW reports grant/research support from and serving as a consultant for Celltrion, Galapagos, and Gilead Sciences. WFCR reports serving as a consultant for Gilead Sciences. DvdH reports serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Cyxone, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Co., Galapagos, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and UCB Pharma; and is director of Imaging Rheumatology BV. DWTC reports receiving grants from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and Sanofi; and serving as a consultant for AbbVie and Pfizer. WS reports receiving consulting fees from Janssen Research and Development, and research support from GlaxoSmithKline. JK reports research grants paid to his institution from AbbVie, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and UCB; and has received personal fees from AbbVie, Alvotech,Suisse AG, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH, Celltrion Healthcare Co., Janssen Biotech, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Mylan, Novartis AG, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, and UCB. AC reports no conflicts of interest. BB, FM, ZY, and YG are shareholders and employees of Gilead Sciences. CT is a shareholder and employee of Galapagos NV. JSS is a shareholder and former employee of Gilead Sciences; and current employee and shareholder of Pandion Therapeutics. NM is a shareholder and former employee of Gilead Sciences, and current employee of Ichnos Sciences. AJ is a shareholder and former employee of Gilead Sciences. ODM reports serving on a speaker’s bureau for Americas Health Foundation, Amgen, and Pfizer. RBML reports serving as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Co., Galapagos NV, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. TA reports grant/research support from AbbVie, Alexion, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., and Pfizer; and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and UCB Japan Co.; and has served on a speakers bureau for AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Eisai Co., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Pfizer, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., and UCB Japan Co. GRB reports serving as a consultant and on a speaker’s bureau for AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Co., Pfizer, and Gilead Sciences.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

