180-day readmission risk model for older adults with acute myocardial infarction: the SILVER-AMI study
- PMID: 33452007
- PMCID: PMC7813425
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001442
180-day readmission risk model for older adults with acute myocardial infarction: the SILVER-AMI study
Erratum in
-
Correction: 180-day readmission risk model for older adults with acute myocardial infarction: the SILVER-AMI study.Open Heart. 2021 Oct;8(2):1. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2020-001442corr1. Open Heart. 2021. PMID: 34663752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To develop a 180-day readmission risk model for older adults with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) that considered a broad range of clinical, demographic and age-related functional domains.
Methods: We used data from ComprehenSIVe Evaluation of Risk in Older Adults with AMI (SILVER-AMI), a prospective cohort study that enrolled participants aged ≥75 years with AMI from 94 US hospitals. Participants underwent an in-hospital assessment of functional impairments, including cognition, vision, hearing and mobility. Clinical variables previously shown to be associated with readmission risk were also evaluated. The outcome was 180-day readmission. From an initial list of 72 variables, we used backward selection and Bayesian model averaging to derive a risk model (N=2004) that was subsequently internally validated (N=1002).
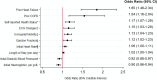
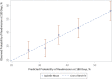
Results: Of the 3006 SILVER-AMI participants discharged alive, mean age was 81.5 years, 44.4% were women and 10.5% were non-white. Within 180 days, 1222 participants (40.7%) were readmitted. The final risk model included 10 variables: history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, history of heart failure, initial heart rate, first diastolic blood pressure, ischaemic ECG changes, initial haemoglobin, ejection fraction, length of stay, self-reported health status and functional mobility. Model discrimination was moderate (0.68 derivation cohort, 0.65 validation cohort), with good calibration. The predicted readmission rate (derivation cohort) was 23.0% in the lowest quintile and 65.4% in the highest quintile.
Conclusions: Over 40% of participants in our sample experienced hospital readmission within 180 days of AMI. Our final readmission risk model included a broad range of characteristics, including functional mobility and self-reported health status, neither of which have been previously considered in 180-day risk models.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; epidemiology; health care; outcome assessment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SIC receives funding for her work as a reviewer for the CVS Caremark Clinical Pharmacy Program for the state of Connecticut.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
