Impact of baseline body mass index on the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 33452181
- PMCID: PMC7813423
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001486
Impact of baseline body mass index on the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: This post-hoc analysis explored the impact of body mass index (BMI) on tofacitinib efficacy/safety in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Data were pooled from two phase 3 studies (NCT01877668; NCT01882439). Analyses included patients randomised to tofacitinib 5/10 mg twio times a day or placebo, stratified by baseline BMI: <25 kg/m2, ≥25-<30 kg/m2, ≥30-<35 kg/m2 or ≥35 kg/m2. Endpoints (month 3): American College of Rheumatology (ACR20/50/70), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75 response rates; dactylitis/enthesitis resolution rates; changes from baseline Short Form-36 Health Survey version 2 (SF-36v2) Physical/Mental Component Summary (PCS) scores and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) total score. Safety was also reported.
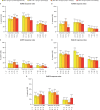
Results: Analysis included 710 patients; 43.8% were obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2). Tofacitinib demonstrated higher efficacy response rates at month 3, compared with placebo, regardless of baseline BMI. Generally, ACR20/50/70 and HAQ-DI response rates, enthesitis resolution rates and changes from baseline in SF-36v2 PCS score and FACIT-F total score (month 3) were reduced in patients with baseline BMI ≥35 kg/m2 versus patients with lower BMIs. Elevated alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase levels were reported in patients with baseline BMI ≥35 kg/m2 receiving tofacitinib 5 mg but not 10 mg two times a day.
Conclusion: Tofacitinib demonstrated greater efficacy than placebo in patients with PsA, regardless of baseline BMI. For all treatment arms, reduced efficacy was observed in patients with baseline BMI ≥35 kg/m2. Safety was generally comparable across BMI categories, although the effect of tofacitinib on liver enzymes in patients with baseline BMI ≥35 kg/m2 was inconclusive.
Keywords: arthritis; autoimmune diseases; inflammation; psoriatic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JTG has received research grants from Pfizer; and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Gilead and UCB. AO has received research grants from Amgen (to Forward/National Databank), Novartis (to the University of Pennsylvania) and Pfizer Inc (to the University of Pennsylvania); and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Corrona, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company and UCB. AO’s husband has received royalties from Novartis. JJG-R has received funding from Pfizer. PSH has received research grants from AbbVie, Janssen and Novartis; and honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Galapagos, Janssen, Pfizer and UCB. RG, LS, PY, WJ, RM and DG are employees and shareholders of Pfizer. CR has received research grants from AbbVie, Amgen and UCB; and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization Global health Observatory (GHO) data, 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/bmi_text/en/ [Accessed 21 May 2020].
-
- Singh I, Rajagopalan S, Srinivasan A, et al. . Preoperative statin therapy is associated with lower requirement of renal replacement therapy in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2013;17:345–52. 10.1093/icvts/ivt178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
