Elucidating different pattern of immunoregulation in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice and their F1 progeny
- PMID: 33452272
- PMCID: PMC7810711
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79477-7
Elucidating different pattern of immunoregulation in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice and their F1 progeny
Abstract
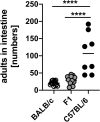
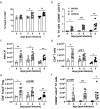
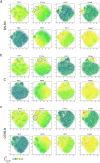
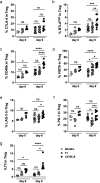
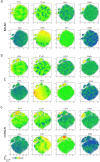
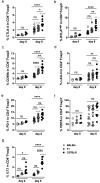
Helminths are large multicellular parasites that infect one quarter of the human population. To prolong their survival, helminths suppress the immune responses of their hosts. Strongyloides ratti delays its expulsion from the gut by induction of regulatory circuits in a mouse strain-specific manner: depletion of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Treg) improves the anti-S. ratti immunity in BALB/c but not in C57BL/6 mice. In the current study we compare the hierarchy of immunoregulatory pathways in BALB/c, C57BL/6 mice and their F1 progeny (BALB/c × C57BL/6). Using multicolor flow cytometry, we show that S. ratti induces a distinct pattern of inhibitory checkpoint receptors by Foxp3+ Treg and Foxp3- T cells. Intensity of expression was highest in C57BL/6 and lowest in BALB/c mice, while the F1 cross had an intermediate phenotype or resembled BALB/c mice. Treg subsets expanded during infection in all three mouse strains. Similar to BALB/c mice, depletion of Treg reduced intestinal parasite burden and increased mucosal mast cell activation in S. ratti-infected F1 mice. Our data indicate that Treg dominate the regulation of immune responses in BALB/c and F1 mice, while multiple regulatory layers exist in C57BL/6 mice that may compensate for the absence of Treg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

