Thermal transformation of polar into less-polar ginsenosides through demalonylation and deglycosylation in extracts from ginseng pulp
- PMID: 33452317
- PMCID: PMC7810680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81079-w
Thermal transformation of polar into less-polar ginsenosides through demalonylation and deglycosylation in extracts from ginseng pulp
Abstract
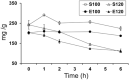
The present study was conducted to qualitatively and quantitatively elucidate dynamic changes of ginsenosides in ginseng pulp steamed under different temperatures (100 or 120 °C) for different durations (1-6 h) through UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and HPLC with the aid of as numerous as 18 authentic standards of ginsenosides. Results show that levels of eight polar ginsenosides (i.e., Rg1, Re, Rb1, Rc, Rb2, Rb3, F1, and Rd) declined but those of 10 less-polar ginsenosides [i.e., Rf, Rg2, 20(S)-Rh1, 20(R)-Rg2, F4, 20(S)-Rg3, 20(R)-Rg3, PPT, Rg5, and 20(R)-Rh2] elevated with increases of both steaming temperature and duration; the optimum steaming conditions for achieving the highest total ginsenosides were 100 °C for 1 h. Particular, 20(R)-Rg3, a representative less-polar ginsenoside with high bioactivity such as potent anti-cancer effect, increased sharply but Re, the most abundant polar ginsenoside in fresh ginseng pulp, decreased dramatically. More importantly, ginsenoside species enhanced from 18 to 42 after steaming, mainly due to transformation of polar into less-polar ginsenosides. Furthermore, four malonyl-ginsenosides were detected in fresh ginseng pulps and ten acetyl-ginsenosides were formed during steaming, demonstrating that demalonylation and acetylation of ginsenosides were the dominant underling mechanisms for transformation of polar into less-polar ginsenosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Singh P, Kim YJ, Wang C, Mathiyalagan R, Yang DC. The development of a green approach for the biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by using Panax ginseng root extract, and their biological applications. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016;44:1150–1157. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, et al. The integration of GC-MS and LC-MS to assay the metabolomics profiling in Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius reveals a tissue- and species-specific connectivity of primary metabolites and ginsenosides accumulation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017;135:176–185. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.12.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

