Memory-specific correlated neuronal activity in higher-order auditory regions of a parrot
- PMID: 33452344
- PMCID: PMC7810846
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80726-y
Memory-specific correlated neuronal activity in higher-order auditory regions of a parrot
Abstract
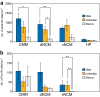
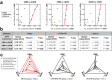
Male budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus) are open-ended learners that can learn to produce new vocalisations as adults. We investigated neuronal activation in male budgerigars using the expression of the protein products of the immediate early genes zenk and c-fos in response to exposure to conspecific contact calls (CCs: that of the mate or an unfamiliar female) in three subregions (CMM, dNCM and vNCM) of the caudomedial pallium, a higher order auditory region. Significant positive correlations of Zenk expression were found between these subregions after exposure to mate CCs. In contrast, exposure to CCs of unfamiliar females produced no such correlations. These results suggest the presence of a CC-specific association among the subregions involved in auditory memory. The caudomedial pallium of the male budgerigar may have functional subdivisions that cooperate in the neuronal representation of auditory memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

