CUL3 E3 ligases in plant development and environmental response
- PMID: 33452490
- PMCID: PMC8932378
- DOI: 10.1038/s41477-020-00833-6
CUL3 E3 ligases in plant development and environmental response
Abstract
Thirty years of research have revealed the fundamental role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in diverse aspects of cellular regulation in eukaryotes. The ubiquitin-protein ligases or E3s are central to the ubiquitin-proteasome system since they determine the specificity of ubiquitylation. The cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) constitute one large class of E3s that can be subdivided based on the cullin isoform and the substrate adapter. SCF complexes, composed of CUL1 and the SKP1/F-box protein substrate adapter, are perhaps the best characterized in plants. More recently, accumulating evidence has demonstrated the essential roles of CRL3 E3s, consisting of a CUL3 protein and a BTB/POZ substrate adaptor. In this Review, we describe the variety of CRL3s functioning in plants and the wide range of processes that they regulate. Furthermore, we illustrate how different classes of E3s may cooperate to regulate specific pathways or processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
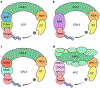

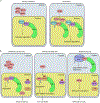
References
-
- Buccitelli C & Selbach M mRNAs, proteins and the emerging principles of gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Genet 21, 630–644 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Hua ZH & Vierstra RD The cullin–RING ubiquitin–protein ligases. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 62, 299–334 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Vierstra RD The ubiquitin–26S proteasome system at the nexus of plant biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 10, 385–397 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Chen L & Hellmann H Plant E3 ligases: flexible enzymes in a sessile world. Mol. Plant 6, 1388–1404 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

