Disease-duration based comparison of subsets of immune cells in SARS CoV-2 infected patients presenting with mild or severe symptoms identifies prognostic markers for severity
- PMID: 33452858
- PMCID: PMC8014065
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.402
Disease-duration based comparison of subsets of immune cells in SARS CoV-2 infected patients presenting with mild or severe symptoms identifies prognostic markers for severity
Abstract
Introduction: Infection with SARS-CoV-2 leads to a spectrum of symptoms. Understanding the basis for severity remains crucial for better management and therapy development. So far, older age, associated-comorbidities, and IL-6 have been associated with severity/mortality.
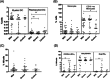
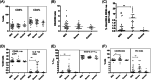
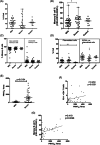
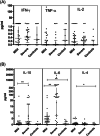
Materials and methodology: As a primary step, we analyzed the frequency and functional profile of innate immune cells (NK cells/dendritic cells/monocytes) and adaptive immunity-driving lymphocytes (B cells/T cells/follicular T helper cells) by flow cytometry. Sixty cases of SARS CoV-2 infection (25 severe, 35 mild) and ten healthy subjects without SARS CoV-2 IgG were included. Disease-duration based analysis of immune profile was explored for early events differentiating the two disease forms. Neutralizing antibody titers were determined by PRNT.
Results and conclusion: Disease severity was found to be associated with impaired maturation of mDCs and hyperactivation of NK, follicular T helper cells, and CD8 T cells. Lower IL-21 receptor expression on memory B cells indicated an imbalance in IL-21/IL-21 R ratio. Lower BCMA positive plasmablast cells in severe cases did suggest a probable absence of long-term humoral immunity. Multivariate analysis revealed a progressive association of PD-1+CD4 T cells with PRNT50 titers. Thus, in addition to identifying probable prognostic markers for severity, our study emphasizes the definite need for in-depth viral antigen-specific functional analyses in a larger patient cohort and with multiple sampling.
Keywords: PRNT50; SARS CoV-2; adaptive immune cells; disease severity; innate immune cells.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Dasbor WHO Coronavirus Disease. WHO. https://covid19.who.int
-
- Zhang X, Tan Y, Ling Y, et al. Viral and host factors related to the clinical outcome of COVID‐19. Nature. 2020;583(7816):437‐440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

