Long-Term Mental Health and Quality of Life Outcomes of Neonatal Insults in Kilifi, Kenya
- PMID: 33452950
- PMCID: PMC8924086
- DOI: 10.1007/s10578-020-01079-1
Long-Term Mental Health and Quality of Life Outcomes of Neonatal Insults in Kilifi, Kenya
Abstract
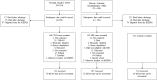
We examined the mental health and quality of life (QoL) outcomes and their correlates of school-aged survivors of neonatal jaundice (NNJ), hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), and a comparison group. The Child Behavior Checklist and the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory were administered to assess the mental health and QoL of 375 children (134 with NNJ, 107 with HIE, and 134 comparison group) aged 6 to 12 years [Median age 9 (interquartile range 7 to 11)]. The results showed that survivors of NNJ and HIE have mental health problems and QoL similar to the comparison group. Maternal mental health was the predominant covariate of mental health and QoL in survivors of NNJ and HIE. This result could indicate that mothers with mental health problems are more likely to have children with mental health issues, but also that caring for children with these adversities may affect mental health well-being of the caregivers. There is a need for early mental health screening and psychosocial intervention for caregivers and their children to enhance both their mental health and QoL.
Keywords: Behaviour; Emotions; Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; Neonatal jaundice.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kurinczuk JJ, White-Koning M, Badawi N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86(6):329–338. - PubMed
-
- Perlman JM. Summary proceedings from the neurology group on hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2006;117(Supplement 1):S28–S33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources