Effects of offloading devices on static and dynamic balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review
- PMID: 33452959
- PMCID: PMC8087551
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-020-09619-9
Effects of offloading devices on static and dynamic balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review
Abstract
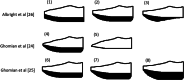
Patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) usually have reduced somatosensory information and altered perception in feet and ankles. Somatosensory information acts as feedback for movement control and loss of somatosensation leads to altered plantar pressure patterns during gait and stance. Offloading devices are used to reduce peak plantar pressure and prevent diabetic foot ulcers. However, offloading devices can unfortunately have negative effects on static and dynamic balance. It is important to investigate these unwanted effects, since patient with DPN already are at high risk of falling and offloading devices could potentially increase this risk. The aim of this systematic review is to investigate the effects of plantar offloading devices used for ulcer prevention on their role in static and dynamic balance control in patients with DPN. PubMed and Embase were systematically searched using relevant search terms. After title selection, abstract selection, and full-text selection only five articles could be included for further analysis. Two articles included static balance measurements, two articles included dynamic balance measurements, and one article included both. Results suggested that static balance control is reduced when rocker bottom shoes and different insole configurations are used, however, toe-only rockers showed less evidence for reduced static balance control. There was no evidence for reduced dynamic balance control in combination with offloading devices. However, these results should be interpreted with care, since the number of studies was very small and the quality of the studies was moderate. Future research should evaluate balance in combination with different offloading devices, so that clinicians subscribing them are more aware of their potential unwanted consequences.
Keywords: Balance; Neuropathy; Offloading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(2):217–228. - PubMed
-
- Kisozi T, Mutebi E, Kisekka M, Lhatoo S, Sajatovic M, Kaddumukasa M, Nakwagala FN, Katabira E. Prevalence, severity and factors associated with peripheral neuropathy among newly diagnosed diabetic patients attending Mulago hospital: a cross-sectional study. Afr Health Sci. 2017;17(2):463–473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh PR, Derr JA, Ulbrecht JS, Maser RE, Orchard TJ. Problems with gait and posture in neuropathic patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1992;9(5):469–474. - PubMed
-
- McKeon PO, Hertel J. Diminished plantar cutaneous sensation and postural control. Percept Mot Skills. 2007;104(1):56–66. - PubMed
-
- Veves A, Murray HJ, Young MJ, Boulton AJM. The risk of foot ulceration in diabetic patients with high foot pressure: a prospective study. Diabetologia. 1992;35(7):660–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

