A narrative review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): clinical, epidemiological characteristics, and systemic manifestations
- PMID: 33453010
- PMCID: PMC7811158
- DOI: 10.1007/s11739-020-02616-5
A narrative review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): clinical, epidemiological characteristics, and systemic manifestations
Abstract
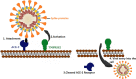
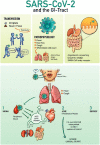
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an emerging infectious disease which has had a rapid surge in cases and deaths since it is first documented in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. COVID-19 is caused by the Betacoronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). SARS-CoV-2 uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, which is highly expressed in the human lower respiratory tract but also in other tissues, as the cellular entry receptor. Thus, COVID-19 mainly affects the respiratory system but can cause damage to other body systems, including the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, renal, and central nervous systems. We review the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of the infection, focusing on our current understanding of the disease mechanisms and their translation to clinical outcomes, as well as adverse effects on different body systems. We also discuss the epidemiology pathogenesis, clinical, and multi-organ consequences, and highlight some of the research gaps regarding COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical symptoms; Coronavirus; Epidemiology; SARS-CoV-2; Transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19.Online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/whodirector- general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19. Accessed 14 Aug 2020
-
- Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report – 22 (World Health Organization); https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 14 Aug 2020
-
- . World Health Organization. Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2003 Dec. Available from: https://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table2004_04_21/en. Accessed 14 Aug 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous