Evolution, folding, and design of TIM barrels and related proteins
- PMID: 33453500
- PMCID: PMC8250049
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.12.007
Evolution, folding, and design of TIM barrels and related proteins
Abstract
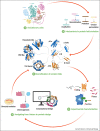
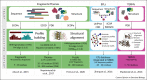
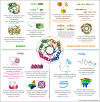
Proteins are chief actors in life that perform a myriad of exquisite functions. This diversity has been enabled through the evolution and diversification of protein folds. Analysis of sequences and structures strongly suggest that numerous protein pieces have been reused as building blocks and propagated to many modern folds. This information can be traced to understand how the protein world has diversified. In this review, we discuss the latest advances in the analysis of protein evolutionary units, and we use as a model system one of the most abundant and versatile topologies, the TIM-barrel fold, to highlight the existing common principles that interconnect protein evolution, structure, folding, function, and design.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Eck R.V., Dayhoff M.O. Evolution of the structure of ferredoxin based on living relics of primitive amino acid sequences. Science. 1966;152:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Fetrow J.S., Godzik A. Function driven protein evolution. A possible proto-protein for the RNA-binding proteins. Pac Symp Biocomput. 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

