Lassa-VSV chimeric virus targets and destroys human and mouse ovarian cancer by direct oncolytic action and by initiating an anti-tumor response
- PMID: 33453650
- PMCID: PMC8451984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2020.10.009
Lassa-VSV chimeric virus targets and destroys human and mouse ovarian cancer by direct oncolytic action and by initiating an anti-tumor response
Abstract
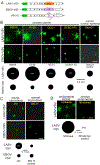
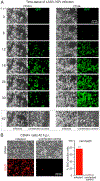
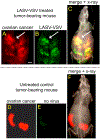
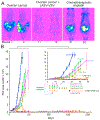
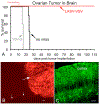
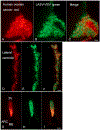
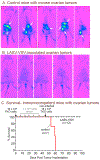
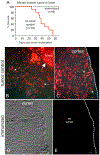
Ovarian cancer is the third most common female cancer, with poor survival in later stages of metastatic spread. We test a chimeric virus consisting of genes from Lassa and vesicular stomatitis viruses, LASV-VSV; the native VSV glycoprotein is replaced by the Lassa glycoprotein, greatly reducing neurotropism. Human ovarian cancer cells in immunocompromised nude mice were lethal in controls. Chemotherapeutic paclitaxel and cisplatin showed modest cancer inhibition and survival extension. In contrast, a single intraperitoneal injection of LASV-VSV selectively infected and killed ovarian cancer cells, generating long-term survival. Mice with human ovarian cancer cells in brain showed rapid deterioration; LASV-VSV microinjection into brain blocked cancer growth, and generated long-term survival. Treatment of immunocompetent mice with infected mouse ovarian cancer cells blocked growth of non-infected ovarian cancer cells peritoneally and in brain. These results suggest LASV-VSV is a viable candidate for further study and may be of use in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
Av has a financial interest in Implicyte. Other authors declare no conflict.
Figures
References
-
- Akeson M, Zetterqvist BM, Dahllof K, Brannstrom M, Horvath G, 2008. Effect of adjuvant paclitaxel and carboplatin for advanced stage epithelial ovarian cancer: a population-based cohort study of all patients in western Sweden with long-term follow-up. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand 87, 1343–1352 - PubMed
-
- Alvero AB, Fishman DA, Qumsiyeh MB, Garg M, Kacinski BM, Sapi E, 2004. Telomerase prolongs the lifespan of normal human ovarian surface epithelial cells without inducing neoplastic phenotype. J. Soc. Gynecol. Invest 11, 553–561. - PubMed
-
- Alvero AB, Heaton A, Lima E, Pitruzzello M, Sumi N, Yang-Hartwich Y, Cardenas C, Steinmacher S, Silasi DA, Brown D, Mor G, 2016. TRX-E-002–1 induces c-Jun-dependent apoptosis in ovarian cancer stem cells and prevents recurrence in vivo. Mol. Canc. Therapeut 15, 1279–1290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

