Effect of nondipper hypertension on coronary artery disease progression in patients with chronic coronary syndrome
- PMID: 33453712
- PMCID: PMC8283452
- DOI: 10.3906/sag-2011-225
Effect of nondipper hypertension on coronary artery disease progression in patients with chronic coronary syndrome
Abstract
Background/aim: It has been suggested that there is a significant progress in coronary artery disease (CAD) by many pathophysiological mechanisms. Nondipper hypertension (NDH) has been shown to have higher target organ damage and have a higher rate of cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. In this study, we investigated the effect of nondipper hypertension on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis.
Materials and methods: A total of 186 patients who underwent coronary angiography twice between 6 months and 3 years were included in the study. Coronary angiography was repeated on the admission day due to angina or positive exercise test and the patients were divided into groups.
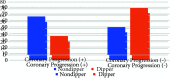
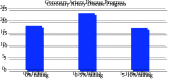
Results: Progression of coronary artery disease was detected in 58 of 186 patients. Seventy-one of the total patients were found to be nondipper hypertensive. Nondipper hypertension, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, low-density lipoprotein, and total cholesterol were found to be effective in the progression of CAD. Among these parameters, it was seen that nondipper hypertension and hyperlipidemia were the most important independent risk factors.
Conclusion: Coronary artery disease is a progressive disease, and this progression depends on many reasons. In our study, we showed that nondipper hypertension is a new parameter that is effective in CAD progression.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; progression; nondipper hypertension.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest regarding the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The frequency and risk of preclinical coronary artery disease detected using multichannel cardiac computed tomography in patients with ischemic stroke.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33(3):286-94. doi: 10.1159/000334980. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 22286013
-
Coronary artery disease among hypertensive patients undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2009 Mar;10(3):252-6. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e3283240486. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2009. PMID: 19262212
-
Relationship between vitamin D deficiency and nondipper hypertension.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2013;35(1):45-9. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2012.689045. Epub 2012 May 17. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 22594967
-
Hypertensive patients with false-positive thallium-201 scintigraphic results in the infero-posterior wall are in high risk for coronary artery disease development.Int J Cardiol. 2007 Apr 25;117(2):178-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.06.011. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Int J Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 16904776 Clinical Trial.
-
Sex differences in independent factors associated with coronary artery disease.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2014 Nov;126(21-22):718-26. doi: 10.1007/s00508-014-0602-9. Epub 2014 Sep 13. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 25216757
Cited by
-
Relationships between Easily Available Biomarkers and Non-Dipper Blood Pressure Pattern in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 25;13(3):640. doi: 10.3390/life13030640. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Millar-Craig MW Bishop CN Raftery EB Circadian variation of blood-pressure. Lancet . 1978;1:795–797. - PubMed
-
- Fujii T Uzu T Nishimura M Takeji M Kuroda S Circadian rhythm of natriuresis is disturbed in nondipper type of essential hypertension. American Journal of Kidney Diseases . 1999;33:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Pierdomenico SD Bucci A Costantini F Lapenna D Cuccurullo F Circadian blood pressure changes and myocardial ischemia in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. Journal of The American College of Cardiology . 1998;31:1627–1634. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous