Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the detection and management of colorectal cancer in England: a population-based study
- PMID: 33453763
- PMCID: PMC7808901
- DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00005-4
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the detection and management of colorectal cancer in England: a population-based study
Abstract
Background: There are concerns that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a negative effect on cancer care but there is little direct evidence to quantify any effect. This study aims to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the detection and management of colorectal cancer in England.
Methods: Data were extracted from four population-based datasets spanning NHS England (the National Cancer Cancer Waiting Time Monitoring, Monthly Diagnostic, Secondary Uses Service Admitted Patient Care and the National Radiotherapy datasets) for all referrals, colonoscopies, surgical procedures, and courses of rectal radiotherapy from Jan 1, 2019, to Oct 31, 2020, related to colorectal cancer in England. Differences in patterns of care were investigated between 2019 and 2020. Percentage reductions in monthly numbers and proportions were calculated.
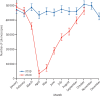
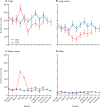
Findings: As compared to the monthly average in 2019, in April, 2020, there was a 63% (95% CI 53-71) reduction (from 36 274 to 13 440) in the monthly number of 2-week referrals for suspected cancer and a 92% (95% CI 89-95) reduction in the number of colonoscopies (from 46 441 to 3484). Numbers had just recovered by October, 2020. This resulted in a 22% (95% CI 8-34) relative reduction in the number of cases referred for treatment (from a monthly average of 2781 in 2019 to 2158 referrals in April, 2020). By October, 2020, the monthly rate had returned to 2019 levels but did not exceed it, suggesting that, from April to October, 2020, over 3500 fewer people had been diagnosed and treated for colorectal cancer in England than would have been expected. There was also a 31% (95% CI 19-42) relative reduction in the numbers receiving surgery in April, 2020, and a lower proportion of laparoscopic and a greater proportion of stoma-forming procedures, relative to the monthly average in 2019. By October, 2020, laparoscopic surgery and stoma rates were similar to 2019 levels. For rectal cancer, there was a 44% (95% CI 17-76) relative increase in the use of neoadjuvant radiotherapy in April, 2020, relative to the monthly average in 2019, due to greater use of short-course regimens. Although in June, 2020, there was a drop in the use of short-course regimens, rates remained above 2019 levels until October, 2020.
Interpretation: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a sustained reduction in the number of people referred, diagnosed, and treated for colorectal cancer. By October, 2020, achievement of care pathway targets had returned to 2019 levels, albeit with smaller volumes of patients and with modifications to usual practice. As pressure grows in the NHS due to the second wave of COVID-19, urgent action is needed to address the growing burden of undetected and untreated colorectal cancer in England.
Funding: Cancer Research UK, the Medical Research Council, Public Health England, Health Data Research UK, NHS Digital, and the National Institute for Health Research Oxford Biomedical Research Centre.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Effect of COVID-19 on colorectal cancer care in England.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Mar;6(3):152-154. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00017-0. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33453764 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gastrointestinal sequelae 90 days after discharge for COVID-19.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;6(5):344-346. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00076-5. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33711290 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer care in France.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;6(5):342-343. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00095-9. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33857441 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effect of COVID-19 on the detection and management of colorectal cancer in England.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;6(5):342. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00034-0. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33857442 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cancer Research UK Bowel cancer statistics. 2020. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/st...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

