A structural and kinetic survey of GH5_4 endoglucanases reveals determinants of broad substrate specificity and opportunities for biomass hydrolysis
- PMID: 33454012
- PMCID: PMC7762963
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015328
A structural and kinetic survey of GH5_4 endoglucanases reveals determinants of broad substrate specificity and opportunities for biomass hydrolysis
Abstract
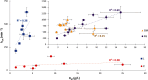
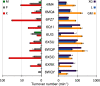
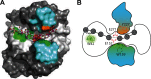
Broad-specificity glycoside hydrolases (GHs) contribute to plant biomass hydrolysis by degrading a diverse range of polysaccharides, making them useful catalysts for renewable energy and biocommodity production. Discovery of new GHs with improved kinetic parameters or more tolerant substrate-binding sites could increase the efficiency of renewable bioenergy production even further. GH5 has over 50 subfamilies exhibiting selectivities for reaction with β-(1,4)-linked oligo- and polysaccharides. Among these, subfamily 4 (GH5_4) contains numerous broad-selectivity endoglucanases that hydrolyze cellulose, xyloglucan, and mixed-linkage glucans. We previously surveyed the whole subfamily and found over 100 new broad-specificity endoglucanases, although the structural origins of broad specificity remained unclear. A mechanistic understanding of GH5_4 substrate specificity would help inform the best protein design strategies and the most appropriate industrial application of broad-specificity endoglucanases. Here we report structures of 10 new GH5_4 enzymes from cellulolytic microbes and characterize their substrate selectivity using normalized reducing sugar assays and MS. We found that GH5_4 enzymes have the highest catalytic efficiency for hydrolysis of xyloglucan, glucomannan, and soluble β-glucans, with opportunistic secondary reactions on cellulose, mannan, and xylan. The positions of key aromatic residues determine the overall reaction rate and breadth of substrate tolerance, and they contribute to differences in oligosaccharide cleavage patterns. Our new composite model identifies several critical structural features that confer broad specificity and may be readily engineered into existing industrial enzymes. We demonstrate that GH5_4 endoglucanases can have broad specificity without sacrificing high activity, making them a valuable addition to the biomass deconstruction toolset.
Keywords: GH5; bioenergy; cellulase; endoglucanase; glycoside hydrolase; polysaccharide; substrate specificity; xyloglucanase.
Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
-
- Oke M. A., Annuar M. S. M., and Simarani K. (2016) Mixed feedstock approach to lignocellulosic ethanol production-prospects and limitations. Bioenerg. Res. 9, 1189–1203 10.1007/s12155-016-9765-8 - DOI

