MiR-27b-3p inhibits the progression of renal fibrosis via suppressing STAT1
- PMID: 33454903
- PMCID: PMC7900087
- DOI: 10.1007/s13577-020-00474-z
MiR-27b-3p inhibits the progression of renal fibrosis via suppressing STAT1
Abstract
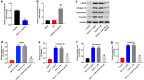
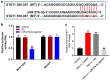
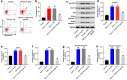
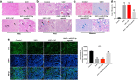
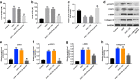
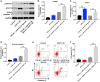
Renal fibrosis is a pathologic change in chronic kidney disease (CKD). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to play an important role in the development of renal fibrosis. However, the biological role of miR-27b-3p in renal fibrosis remains unclear. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the role of miR-27b-3p in the progression of renal fibrosis. In this study, HK-2 cells were stimulated with transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 for mimicking fibrosis progression in vitro. The unilateral ureteric obstruction (UUO)-induced mice renal fibrosis in vivo was established as well. The results indicated that the overexpression of miR-27b-3p significantly inhibited epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in TGF-β1-stimulated HK-2 cells, as shown by the decreased expressions of α-SMA, collagen III, Fibronectin and Vimentin. In addition, overexpression of miR-27b-3p markedly decreased TGF-β1-induced apoptosis in HK-2 cells, as evidenced by the decreased levels of Fas, active caspase 8 and active caspase 3. Meanwhile, dual-luciferase assay showed that miR-27b-3p downregulated signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) expression through direct binding with the 3'-UTR of STAT1. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-27b-3p attenuated UUO-induced renal fibrosis via downregulation of STAT1, α-SMA and collagen III. In conclusion, miR-27b-3p overexpression could alleviate renal fibrosis via suppressing STAT1 in vivo and in vitro. Therefore, miR-27b-3p might be a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Renal fibrosis; Unilateral ureteral obstruction; miR-27b-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate renal fibrosis via delivery of miR-186-5p.Hum Cell. 2022 Jan;35(1):83-97. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00617-w. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Hum Cell. 2022. PMID: 34585365
-
MicroRNA miR-4709-3p targets Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 2 (LATS2) and induces obstructive renal fibrosis through Hippo signaling.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12357-12371. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2002493. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34931960 Free PMC article.
-
miR-130a-3p inhibition protects against renal fibrosis in vitro via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway by targeting SnoN.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Feb;112:104358. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104358. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31836508
-
Epigenetics of progression of chronic kidney disease: fact or fantasy?Semin Nephrol. 2013 Jul;33(4):363-74. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.05.008. Semin Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 24011578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Chronic Kidney Disease: Four Candidates for Clinical Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 7;21(18):6547. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186547. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32906849 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-27b-3p reduces muscle fibrosis during chronic skeletal muscle injury by targeting TGF-βR1/Smad pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jun 2;19(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04733-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38825706 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics reveals the key transcription-related factors mediating obstructive nephropathy in pediatric patients and mice.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2443032. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2443032. Epub 2025 Jan 1. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 39743726 Free PMC article.
-
Normothermic liver perfusion derived extracellular vesicles have concentration-dependent immunoregulatory properties.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Jul;13(7):e12485. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12485. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 39051751 Free PMC article.
-
Acteoside alleviates UUO-induced inflammation and fibrosis by regulating the HMGN1/TLR4/TREM1 signaling pathway.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 18;11:e14765. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14765. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36691481 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Systemic Sclerosis: Involvement in Disease Pathogenesis and Potential Use as Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Biomedicines. 2025 May 16;13(5):1216. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051216. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

