Balancing ecological conservation with socioeconomic development
- PMID: 33454911
- PMCID: PMC8035341
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-020-01448-z
Balancing ecological conservation with socioeconomic development
Abstract
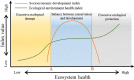
Ecological restoration and conservation are primary components of sustainable development around the world, particularly during the contemporary era of climate change. However, restoration and conservation are not free; they consume huge amounts of resources that would otherwise support social and economic development. Therefore, excessive conservation creates a risk of creating rather than eliminating poverty. Unfortunately, scientists have largely ignored the balance between these contrasting goals. Here, we discuss the concept of finding the threshold that represents a suitable balance between ecological conservation and economic development, thereby maximizing the benefits for both humans and the environment and promoting sustainable development. To demonstrate the concept, we examined China's ecological restoration achievements and discussed some of the unforeseen negative consequences that accompanied these achievements to discuss how future policies could better balance ecological and socioeconomic goals.
Keywords: Conservation threshold; Conservation trap; Degradation trap; Ecosystem degradation; Environmental conservation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simulating the Impact of Future Climate Change and Ecological Restoration on Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services in Two Ecological Shelters and Three Belts in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 26;17(21):7849. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217849. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33114783 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the poverty trap in an ecologically fragile region through ecological engineering: A close-up look at long-term changes in ecosystem services.J Environ Manage. 2024 May;358:120921. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120921. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 38652992
-
Ecosystem water imbalances created during ecological restoration by afforestation in China, and lessons for other developing countries.J Environ Manage. 2016 Dec 1;183(Pt 3):843-849. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.096. Epub 2016 Sep 22. J Environ Manage. 2016. PMID: 27666647
-
Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China.J Environ Manage. 2008 Sep;88(4):1249-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.06.019. Epub 2007 Sep 4. J Environ Manage. 2008. PMID: 17767999 Review.
-
China's coastal wetlands: conservation history, implementation efforts, existing issues and strategies for future improvement.Environ Int. 2015 Jun;79:25-41. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Environ Int. 2015. PMID: 25771079 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Contemporary Challenges and Debates on Chinese Food Security: Integrating Priorities, Trade-Offs, and Policy Pathways.Foods. 2025 Mar 19;14(6):1057. doi: 10.3390/foods14061057. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40232105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Spatial Coupling Coordination Development: Identifying Land System States from the Adaptation-Conflict Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 26;20(1):373. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010373. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612695 Free PMC article.
-
Governance of China's Potatso National Park Influenced by Local Community Participation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 1;20(1):807. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010807. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36613127 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities in Aligning Conservation with Development in China's National Parks: A Narrative Literature Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 6;19(19):12778. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912778. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36232085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Relationship between Ecosystem Services under Different Socio-Economic Driving Degrees.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 1;19(23):16105. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316105. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36498179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastan M, Khorshid-Doust RR, Sisi SD, Ahmadvand A. Sustainable development of agriculture: A system dynamics model. Kybernetes. 2017;47:142–162. doi: 10.1108/K-01-2017-0003. - DOI
-
- Cao S, Chen L, Shankman D, Wang C, Wang X, Zhang H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth Science Reviews. 2011;104:240–245. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.11.002. - DOI
-
- Cao S, Suo X, Xia C. Payoff from afforestation under the Three-North Shelter Forest Program. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2020;256:120461. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120461. - DOI
-
- Cao S, Xia C, Xian J, Guo H, Zheng H. Payoff of the grain for green policy. Journal of Applied Ecology. 2020;57:1180–1188. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.13608. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

