Long-term effects of weight-reducing drugs in people with hypertension
- PMID: 33454957
- PMCID: PMC8094237
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007654.pub5
Long-term effects of weight-reducing drugs in people with hypertension
Abstract
Background: This is the third update of this review, first published in July 2009. All major guidelines on treatment of hypertension recommend weight loss; anti-obesity drugs may be able to help in this respect.
Objectives: Primary objectives: To assess the long-term effects of pharmacologically-induced reduction in body weight in adults with essential hypertension on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular morbidity, and adverse events (including total serious adverse events, withdrawal due to adverse events, and total non-serious adverse events).. Secondary objectives: To assess the long-term effects of pharmacologically-induced reduction in body weight in adults with essential hypertension on change from baseline in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and on body weight reduction.
Search methods: For this updated review, the Cochrane Hypertension Information Specialist searched the following databases for randomised controlled trials up to March 2020: the Cochrane Hypertension Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE (from 1946), Embase (from 1974), the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.gov. The searches had no language restrictions. We contacted authors of relevant papers about further published and unpublished work.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials of at least 24 weeks' duration in adults with hypertension that compared approved long-term weight-loss medications to placebo. DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS: Two review authors independently selected studies, assessed risks of bias, and extracted data. Where appropriate and in the absence of significant heterogeneity between studies (P > 0.1), we pooled studies using a fixed-effect meta-analysis. When heterogeneity was present, we used the random-effects method and investigated the cause of the heterogeneity.
Main results: This third update of the review added one new trial, investigating the combination of naltrexone/bupropion versus placebo. Two medications, which were included in the previous versions of this review (rimonabant and sibutramine) are no longer considered relevant for this update, since their marketing approval was withdrawn in 2010 and 2009, respectively. The number of included studies in this review update is therefore six (12,724 participants in total): four RCTs comparing orlistat to placebo, involving a total of 3132 participants with high blood pressure and a mean age of 46 to 55 years; one trial comparing phentermine/topiramate to placebo, involving 1305 participants with high blood pressure and a mean age of 53 years; and one trial comparing naltrexone/bupropion to placebo, involving 8283 participants with hypertension and a mean age of 62 years. We judged the risks of bias to be unclear for the trials investigating orlistat or naltrexone/bupropion. and low for the trial investigating phentermine/topiramate. Only the study of naltrexone/bupropion included cardiovascular mortality and morbidity as predefined outcomes. There were no differences in the rates of all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, major cardiovascular events, or serious adverse events between naltrexone/bupropion and placebo. The incidence of overall adverse events was significantly higher in participants treated with naltrexone/bupropion. For orlistat, the incidence of gastrointestinal side effects was consistently higher compared to placebo. The most frequent side effects with phentermine/topiramate were dry mouth and paraesthesia. After six to 12 months, orlistat reduced systolic blood pressure compared to placebo by mean difference (MD) -2.6 mm Hg (95% confidence interval (CI) -3.8 to -1.4 mm Hg; 4 trials, 2058 participants) and diastolic blood pressure by MD -2.0 mm Hg (95% CI -2.7 to -1.2 mm Hg; 4 trials, 2058 participants). After 13 months of follow-up, phentermine/topiramate decreased systolic blood pressure compared to placebo by -2.0 to -4.2 mm Hg (1 trial, 1030 participants) (depending on drug dosage), and diastolic blood pressure by -1.3 to -1.9 mm Hg (1 trial, 1030 participants) (depending on drug dosage). There was no difference in the change in systolic or diastolic blood pressure between naltrexone/bupropion and placebo (1 trial, 8283 participants). We identified no relevant studies investigating liraglutide or lorcaserin in people with hypertension.
Authors' conclusions: In people with elevated blood pressure, orlistat, phentermine/topiramate and naltrexone/bupropion reduced body weight; the magnitude of the effect was greatest with phentermine/topiramate. In the same trials, orlistat and phentermine/topiramate, but not naltrexone/bupropion, reduced blood pressure. One RCT of naltrexone/bupropion versus placebo showed no differences in all-cause mortality or cardiovascular mortality or morbidity after two years. The European Medicines Agency refused marketing authorisation for phentermine/topiramate due to safety concerns, while for lorcaserin the application for European marketing authorisation was withdrawn due to a negative overall benefit/risk balance. In 2020 lorcaserin was also withdrawn from the US market. Two other medications (rimonabant and sibutramine) had already been withdrawn from the market in 2009 and 2010, respectively.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Andrea Siebenhofer, Klaus Jeitler, and Karl Horvath were involved in the preparation of a report on the evaluation of the benefits and harms of non‐drug treatment strategies in people with essential hypertension: weight reduction for the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (
Andrea Berghold: none known.
Sebastian Winterholer: none known.
Cornelia Krenn: none known.
Thomas Semlitsch: none known.
Figures
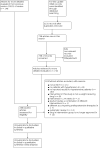
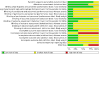
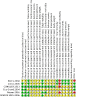
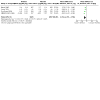















Update of
-
Long-term effects of weight-reducing drugs in people with hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 2;3:CD007654. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007654.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 17;1:CD007654. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007654.pub5. PMID: 26934640 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bakris 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bakris G, Calhoun D, Egan B, Hellmann C, Dolker M, Kingma I, et al. Orlistat improves blood pressure control in obese subjects with treated but inadequately controlled hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2002;20(11):2257-67. - PubMed
Cocco 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cocco G, Pandolfi S, Rousson V. Sufficient weight reduction decreases cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients with the metabolic syndrome: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes (diet and exercise). Heart Drug 2005;5(2):68-74.
CONQUER 2013 {published data only}
-
- Astrup AV, Oppert JM, Peterson CA. Weight loss and improvements in cardiometabolic outcomes with extended-release phentermine/topiramate treatment in overweight/obese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2012;55(Suppl1):S284-S285. [EMBASE: 70888716]
-
- Cheskin J, Bowden CH. Reduction of cardiovascular risk factors by magnitude of weight loss in obese and overweight subjects with >2 comorbidities. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2013;28(Suppl1):S168. [EMBASE: 71292986]
-
- Cheskin LJ, Peterson CA. Improved cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight/obese subjects receiving controlled-release phentermine/topiramate (PHEN/TPM CR). Diabetes 2012;61(Suppl1):A710. [EMBASE: 70799295]
-
- Davidson M, Bowden CH, Day WW. Weight loss and cardiovascular risk reduction over 2 years with controlled-release phentermine-topiramate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2011;57(14, Supplement):E545. [EMBASE: 70400222]
-
- Davidson MH, Tonstad S, Oparil S, Schwiers M, Day WW, Bowden CH. Changes in cardiovascular risk associated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release in participants with comorbidities and a body mass index >27 kg/m(2). American Journal of Cardiology 2013;111(8):1131-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guy‐Grand 2004 {published data only}
-
- Guy-Grand B, Drouin P, Eschwege E, Gin H, Joubert JM, Valensi P. Effects of orlistat on obesity-related diseases - a six-month randomized trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2004;6(5):375-83. - PubMed
Nissen 2016 {published data only}
-
- Buse JB, Smith SR, Gilder K, Shan K, Halseth A. Effect of naltrexone/bupropion on cardiovascular events in overweight and obese participants with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors in a large randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes 2017;66(Supplement 1):A557. [EMBASE: 8024951]
-
- Halseth A, Gilder K, Shan K, Acevedo L, Buse J. Effect on body weight of naltrexone/bupropion in overweight and obese participants with cardiovascular risk factors in a large randomized double-blind study. Obesity Facts 2017;10(Supplement 1):46. [EMBASE: 8024954]
-
- Halseth A, Gilder K, Shan K, Acevedo L, Smith S. Naltrexone/bupropion is well tolerated and had no effect on serious adverse events in participants receiving antidepressant medication, including SSRIs, in a large randomized double-blind study. Obesity Facts 2017;10(Supplement 1):46. [EMBASE: 6521721]
-
- Nissen SE, Wolski KE, Prcela L, Wadden T, Buse JB, Bakris G, et al. Effect of naltrexone-bupropion on major adverse cardiovascular events in overweight and obese patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;315(10):990-1004. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Smith SR, Buse JB, Gilder K, Shan K, Halseth A. Effect on body weight of naltrexone/bupropion in overweight and obese participants with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors in a large, randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes 2017;66(Supplement 1):A556. [EMBASE: 8024952]
XENDOS 2001‐2006 {published data only}
-
- Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (IQWiG). Evaluation of the benefits and harms of non-drug weight-reducing treatment strategies in patients with essential hypertension [Nutzenbewertung nichtmedikamentöser Behandlungsstrategien bei Patienten mit Bluthochdruck: A-Gewichtsreduktion]. iqwig.de/download/A05-21A_Abschlussbericht_Gewichtsreduktion_bei_Bluthoc... 2006:19-119.
-
- Torgerson JS, Arlinger K, Kappi M, Sjöström L. Principles for enhanced recruitment of subjects in a large clinical trial. the XENDOS (XENical in the prevention of Diabetes in Obese Subjects) study experience. Controlled Clinical Trials 2001;22(5):515-25. - PubMed
-
- Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjöström L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care 2004;27(1):155-61. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Apfelbaum 1999 {published data only}
-
- Apfelbaum M, Vague P, Ziegler O, Hanotin C, Thomas F, Leutenegger E. Long-term maintenance of weight loss after a very-low-calorie diet: a randomized blinded trial of the efficacy and tolerability of sibutramine. American Journal of Medicine 1999;106(2):179-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bach 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bach DS, Rissanen AM, Mendel CM, Shepherd G, Weinstein SP, Kelly F, et al. Absence of cardiac valve dysfunction in obese patients treated with sibutramine. Obesity Research 1999;7(4):363-9. - PubMed
Bain 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bain SC, Ahmann A, Rodbard H, Rosenstock J, Lahtela J, De Loredo L, et al. A randomised, placebo-controlled trial of liraglutide as adjunct to basal insulin analogues in subjects with Type 2 diabetes (LIRA-ADD2BASAL). Diabetic Medicine 2015;32(Suppl 1):71. [EMBASE: 71821007]
BLOOM 2010 {published data only}
-
- Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Anderson CM, Sanchez M, Chuang E, Stubbe S, et al. Multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight management. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(3):245-56. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Stubbe S, Anderson CM, Shanahan WR. Lorcaserin reduces body weight in obese and overweight subjects: behavioral modification and lorcaserin for overweight and obesity management, the BLOOM trial. Diabetes 2009;58:LB24. [EMBASE: 70134408]
BLOOM‐DM 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fidler MC, Shazer R, Sanchez, M, Stubbe S, Anderson CM, Shanahan WR. Lorcaserin, a selective 5-HT2C agonist, evaluated as a weight loss agent in obese and overweight patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sulfonylureas or metformin. Diabetes 2011;60:A515. [EMBASE: 70629658]
-
- O'Neil PM, Fidler MC, Sanchez, M, Weissman NJ, Smith SR, Anderson CM, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2011;60:A507. [EMBASE: 70629629]
-
- O'Neil PM, Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Zhang J, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the BLOOM-DM study. Obesity 2012;20(7):1426-36. [PMID: ] - PubMed
BLOSSOM 2011 {published data only}
-
- Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Raether B, Weissman NJ, Smith SR, Shanahan WR, et al, BLOSSOM Clinical Trial Group. A one-year randomized trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in obese and overweight adults: the BLOSSOM trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2011;96(10):3067-77. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bray 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bray GA, Blackburn GL, Ferguson JM, Greenway FL, Jain AK, Mendel CM, et al. Sibutramine produces dose-related weight loss. Obesity Research 1999;7(2):189-98. - PubMed
Broom 2002 {published data only}
-
- Broom I, Wilding J, Stott P, Myers N, UK Multimorbidity Study Group. Randomised trial of the effect of orlistat on body weight and cardiovascular disease risk profile in obese patients: UK Multimorbidity Study. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2002;56(7):494-9. - PubMed
CAMELLIA‐TIMI 2018 {published data only}
-
- Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, McGuire DK, Inzucchi SE, Kuder J, Im K, et al. Cardiovascular safety of lorcaserin in overweight or obese patients. New England Journal of Medicine 2018;379(12):1107-17. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- EUCTR2013-000324-34-PL. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the effect of long-term treatment with BELVIQ (lorcaserin HCl) on the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events and conversion to type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese and overweight Subjects with cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors - CAMELLIA. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=EUCTR2013-000324-34-PL (first received 07 July 2014).
-
- NCT02019264. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the effect of long-term treatment with BELVIQ (Lorcaserin HCl) on the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events and conversion to type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese and overweight subjects with cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk fFactors. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02019264 (first received 24 December 2013).
Christou 2015 {published data only}
-
- Christou GA, Kiortsis DN. The efficacy and safety of the naltrexone/bupropion combination for the treatment of obesity: an update. Hormones 2015;14(3):370-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cohen 2019 {published data only}
COR‐BMOD 2011 {published data only}
-
- O'Neil PM, Wadden TA, Foreyt JP, Clapper B, Burns C, Klassen P, et al. Naltrexone SR/bupropion SR and intensive behavioral modification combination increases the likelihood of achieving early and sustained weight loss and associated improvement in markers of cardiometabolic risk. Obesity 2011;19(Suppl1):S179-80. [EMBASE: 70680332]
COR‐Diabetes 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hollander P, Gupta AK, Plodkowski R, Greenway F, Bay H, Burns C, et al. Effects of naltrexone sustained-release/bupropion sustained-release combination therapy on body weight and glycemic parameters in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013;36:4022-9. [EMBASE: 2014021906] - PMC - PubMed
COR‐I 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fujioka K, Billes SK, Burns C, Harris-Collazo R, Kim DD, Dunayevich E, et al. Weight loss and improvements in markers of metabolic risk in overweight and obese subjects completing 56 weeks of treatment with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR. Diabetes 2011;60:A520-1. [EMBASE: 70629675]
-
- Fujioka K, Greenway FL, Rubino D, Clapper B, Burns C, Klassen P, et al. Completion of 56 weeks of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy increases likelihood of achieving improvements in markers of cardiometabolic risk associated with clinically meaningful weight loss. Obesity 2011;19(Suppl1):S179. [EMBASE: 70680330]
-
- Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, Mudaliar S, Guttadauria M, Erickson J, et al. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010;376(9741):595-605. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- NCT00532779. A multicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study comparing the safety and efficacy of two doses of naltrexone sustained release (SR)/bupropion sustained release (SR) and placebo in obese subjects. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00532779 (first received 20 September 2007).
-
- Plutzky J, Buse J, Chilton R, Mignon L, Burns C, Harris-Collazo R, et al. Response to NB at week 16 is a good predictor of significant week 56 weight loss and improvements in weight-related risk factors. Diabetes 2011;60:A700. [EMBASE: 70630321]
COR‐II 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hill JO, Wyatt H, Billes SK, Burns C, Harris-Collazo R, Dunayevich E, et al. Naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy improves control of eating and reduces food cravings in overweight and obese subjects. Diabetes 2011;60:A506. [EMBASE: 70629625]
-
- Kolotkin RL, Still C, Maier H, Burns C, Harris-Collazo R, Dunayevich E, et al. Naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy reduced weight and improved weight-related quality of life and physical health in overweight and obese subjects. Diabetes 2011;60:A506-7. [EMBASE: 70629628]
-
- Plutzky J, Chilton R, Still C, Burns C, Kim D, Dunayevich E. Weight loss, blood pressure, pulse and circadian patterns with naltrexone sustained-release/bupropion sustained-release combination therapy for obesity. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2011;57(14, Supplement):E517. [EMBASE: 70400194]
-
- Rubino D, Apovian C, Mignon L, Burns C, Harris-Collazo R, Kim D. Effects of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related health risks in overweight/obese women from the COR-II trial. Diabetes 2011;60:A504. [EMBASE: 70629619]
CTRI/2017/05/008655 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2017/05/008655. A clinical study to study the effect of lorcaserin tablets in the treatment of obesity. www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2017/05/008655 (first received 25 May 2017).
Davidson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Davidson MH, Hauptman J, DiGirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D, et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: a randomized controlled trial [see comment] [erratum appears in JAMA 1999 Apr 7;281(13):1174]. JAMA 1999;281(3):235-42. - PubMed
De Castro 2009 {published data only}
-
- De Castro JJ, Dias T, Chambel P, Carvalheiro M, Correia LG, Guerreiro L, et al. A randomized double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of orlistat versus placebo in obese patients with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia. Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia 2009;28(12):1361-74. - PubMed
Derosa 2003 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Mugellini A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of the action of orlistat, fluvastatin, or both ao anthropometric measurements, blood pressure, and lipid profile in obese patients with hypercholesterolemia prescribed a standardized diet. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25(4):1107-22. - PubMed
Derosa 2008 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, D'Angelo A, Salvadeo SA, Ferrari I, Gravina A, Fogari E, et al. Sibutramine effect on metabolic control of obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with pioglitazone. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 2008;57(11):1552-7. - PubMed
Derosa 2010 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Ferrari I, Palumbo I, Randazzo S, D'Angelo A, et al. Effects of one year treatment of sibutramine on insulin resistance parameters in type 2 diabetic patients. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2010;13(3):378-90. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Ferrari I, Palumbo I, Randazzo S, D'Angelo A, et al. Variation of inflammatory parameters after sibutramine treatment compared to placebo in type 2 diabetic patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2011;36(5):592-601. - PubMed
Despres 2005 {published data only}
-
- Despres JP, Golay A, Sjöström L. Effects of rimonabant on metabolic risk factors in overweight patients with dyslipidemia. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(20):2121-34. - PubMed
Despres 2009 {published data only}
-
- Despres JP, Ross R, Boka G, Almeras N, Lemieux I. Effect of rimonabant on the high-triglyceride/low-HDL-cholesterol dyslipidemia, intraabdominal adiposity, and liver fat: the ADAGIO-Lipids trial. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2009;29(3):416-23. - PubMed
Dujovne 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dujovne CA, Zavoral JH, Rowe E, Mendel CM. Effects of sibutramine on body weight and serum lipids: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in 322 overweight and obese patients with dyslipidemia. American Heart Journal 2001;142(3):489-97. - PubMed
EQUIP 2012 {published data only}
Erdmann 2004 {published data only}
-
- Erdmann J, Lippl F, Klose G, Schusdziarra V. Cholesterol lowering effect of dietary weight loss and orlistat treatment - Efficacy and limitations. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2004;19(11):1173-9. - PubMed
EUCTR2013‐002348‐99 {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2013-002348-99. A randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled study of the effect of liraglutide on arterial blood pressure in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=eudract_number:201... (first received 22 September 2014).
Fanghänel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fanghänel G, Cortinas L, Sanchez-Reyes L, Berber A. A clinical trial of the use of sibutramine for the treatment of patients suffering essential obesity. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2000;24(2):144-50. - PubMed
-
- Fanghänel G, Cortinas L, Sanchez-Reyes L, Berber A. Second phase of a double-blind study clinical trial on Sibutramine for the treatment of patients suffering essential obesity: 6 months after treatment cross-over. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2001;25(5):741-7. - PubMed
Fanghänel 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fanghänel G, Cortinas L, Sanchez-Reyes L, Gomez-Santos R, Campos-Franco E, Berber A. Safety and efficacy of sibutramine in overweight Hispanic patients with hypertension. Advances in Therapy 2003;20(2):101-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Faria 2002 {published data only}
-
- Faria AN, Ribeiro Filho FF, Kohlmann NE, Gouvea F Sr, Zanella MT. Effects of sibutramine on abdominal fat mass, insulin resistance and blood pressure in obese hypertensive patients. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2005;7(3):246-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Faria AN, Ribeiro Filho FF, Lerario DD, Kohlmann N, Gouvea Ferreira SR, Zanella MT. Effects of sibutramine on the treatment of obesity in patients with arterial hypertension. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia 2002;78(2):172-80. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Finer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Finer N, James WP, Kopelman PG, Lean ME, Williams G. One-year treatment of obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study of orlistat, a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2000;24(3):306-13. - PubMed
Fujioka 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fujioka K, Seaton TB, Rowe E, Jelinek CA, Raskin P, Lebovitz HE, et al. Weight loss with sibutramine improves glycaemic control and other metabolic parameters in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2000;2(3):175-87. - PubMed
Fujioka 2016 {published data only}
-
- Fujioka K, Plodkowski R, O'Neil PM, Gilder K, Walsh B, Greenway FL. The relationship between early weight loss and weight loss at 1 year with naltrexone er/bupropion er combination therapy. International Journal of oOesity 2016;40(9):1369-75. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gadde 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gadde KM, Pritham Raj Y. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: clinical trials to clinical practice. Current Diabetes Reports 2017;17(5):34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Garvey 2009 {published data only}
-
- Garvey WT, Troupin B, Peterson C, Najarian T, Tam P, Day W. Treatment with VI-0521 (phentermine and topiramate) leads to one year durable glycaemic benefit and weight loss in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52(S1):S77. [EMBASE: 70067664]
-
- Garvey WT, Troupin B, Tam P, Najarian T, Peterson C, Day WW. One-year treatment with VI-0521 in type 2 diabetes demonstrates continued glycemic improvement and weight loss. Diabetes 2009;58(Suppl. 1):A95. [EMBASE: 70136156]
Gentile 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gentile S, Guarina G, Padovano B, Buonocunto F, Gruppo Campano Obesita. Efficacy and safety of a short-time orlistat treatment in obese subjects [Efficacia e sicurezza di impiego di un trattamento a breve termine con orlistat in soggetti obesi]. Annali Italiani di Medicina Interna 2005;20(2):90-6. - PubMed
Ginsberg 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ginsberg DL. Add-on sibutramine for olanzapine-induced weight gain. Primary Psychiatry 2004;11(7):24.
Greenway 2009 {published data only}
-
- Greenway FL, Dunayevich E, Tollefson G, Erickson J, Guttadauria M, Fujioka K, et al. Comparison of combined bupropion and naltrexone therapy for obesity with monotherapy and placebo. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2009;94:4898-906. [EMBASE: 2010011828] - PubMed
Greenway 2016 {published data only}
-
- Greenway FL, Shanahan Wm Fain R, Ma T, Rubino D. Safety and tolerability review of lorcaserin in clinical trials. Clinical Obesity 2016;6(5):285-95. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Halpern 2002 {published data only}
-
- Halpern A, Leite CC, Herszkowicz N, Barbato A, Costa AP. Evaluation of efficacy, reliability, and tolerability of sibutramine in obese patients, with an echocardiographic study. Revista do Hospital das Clinicas; Faculdade de Medicina Da Universidade de Sao Paulo 2002;57(3):98-102. - PubMed
Halpern 2003 {published data only}
-
- Halpern A, Mancini MC, Suplicy H, Zanella MT, Repetto G, Gross J, et al. Latin-American trial of orlistat for weight loss and improvement in glycaemic profile in obese diabetic patients. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2003;5(3):180-8. - PubMed
Halseth 2018 {published data only}
-
- Acevedo LM, Shan K, Fujioka K. Improvement in patient-assessed quality of life, eating behavior, and sexual function after 26 weeks of naltrexone/ bupropion compared with usual care. Obesity Facts 2016;9(Suppl 1):177. [EMBASE: 72315993]
-
- Fujioka, K, Walsh B, Halseth AE, Shan K, Wadden TA. Improvement in patient-assessed quality of life, eating behavior, and sexual function after 26 weeks of naltrexone/bupropion compared with usual care. Diabetes 2015;64(Suppl 1):A308. [EMBASE: 71940993]
-
- Halseth A, Shan K, Chen S. Long-term efficacy of naltrexone/bupropion, administered as recommended in clinical practice. Obesity Facts 2016;9(Suppl 1):178. [EMBASE: 72315729]
-
- Halseth A, Shan K, Fujioka K. Efficacy of naltrexone/bupropion, administered asS recommended in clinical practice, compared with usual care for weight management. Obesity Facts 2016;9(Suppl 1):80-1. [EMBASE: 72315729]
Hauner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hauner H, Meier M, Wendland G, Kurscheid T, Lauterbach K, The SAT Study Group. Weight reduction by sibutramine in obese subjects in primary care medicine: the SAT Study. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes 2004;112(4):201-7. - PubMed
Hauptman 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hauptman J, Lucas C, Boldrin MN, Collins H, Segal KR. Orlistat in the long-term treatment of obesity in primary care settings. Archives of Family Medicine 2000;9(2):160-7. - PubMed
Heinonen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Heinonen MV, Laaksonen DE, Karhu T, Karhunen L, Laitinen T, Kainulainen S, et al. Effect of diet-induced weight loss on plasma apelin and cytokine levels in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2009;19(9):626-33. - PubMed
Hollander 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hollander P. Endocannabinoid blockade for improving glycemic control and lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Medicine 2007;120(2 Suppl 1):S18-28. - PubMed
Hung 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hung YJ, Chen YC, Pei D, Kuo SW, Hsieh CH, Wu LY, et al. Sibutramine improves insulin sensitivity without alteration of serum adiponectin in obese subjects with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine 2005;22(8):1024-30. - PubMed
Jain 2011 {published data only}
James 1997 {published data only}
-
- James WP, Avenell A, Broom J, Whitehead J. A one-year trial to assess the value of orlistat in the management of obesity. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 1997;21 Suppl 3:S24-30. - PubMed
James 2000 {published data only}
-
- James WP, Astrup A, Finer N, Hilsted J, Kopelman P, Rossner S, et al. Effect of sibutramine on weight maintenance after weight loss: a randomised trial. STORM Study Group. Sibutramine Trial of Obesity Reduction and Maintenance [see comment]. Lancet 2000;356(9248):2119-25. - PubMed
Jia 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jia J, Xiong L, Chen S. Trial of lorcaserin for weight management. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(25):2468-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Jordan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jordan J, Astrup AV, Day WW. Effects of phentermine and extended-release topiramate alone and in combination on cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetologia 2012;55:S285. [EMBASE: 70888718]
Kaukua 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kaukua JK, Pekkarinen TA, Rissanen AM. Health-related quality of life in a randomised placebo-controlled trial of sibutramine in obese patients with type II diabetes. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2004;28(4):600-5. - PubMed
KCT0002097 {published data only}
-
- KCT0002097. A 48 weeks, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy and safety of obesity medication on morbid obese and obese patients. www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=KCT0002097 (first received 07 October 2016).
Kelley 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kelley DE, Bray GA, Pi-Sunyer FX, Klein S, Hill J, Miles J, et al. Clinical efficacy of orlistat therapy in overweight and obese patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a 1-year randomized controlled trial [erratum appears in Diabetes Care 2003 Mar;26(3):971]. Diabetes Care 2002;25(6):1033-41. - PubMed
Kern 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kern W. Obesity and weight reduction: current findings on liraglutid 3.0 mg [Gewichtsreduktion bei Adipositas: Aktueller Erkenntnisstand zu Liraglutid 3,0 mg]. Diabetes, Stoffwechsel und Herz 2017;26(2):75-83.
Kim 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kim S. Drugs to treat obesity: do they work? Postgraduate Medical Journal 2016;92(1089):401-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Klassen 2016 {published data only}
-
- Klassen P, Halseth A, Chilton R. Weight loss, blood pressure, pulse, and circadian patterns with prolonged-release naltrexone /bupropion combination therapy for obesity. Obesity Facts 2016;9:245. [EMBASE: 4300320]
-
- Klassen P, Halseth AE, Chilton R. Weight loss, blood pressure, pulse, and circadian patterns with combination prolonged-release naltrexone/bupropion therapy for obesity. Obesity Reviews 2016;17(Supplement 2):69. [EMBASE: 7455004]
LEADER 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bain SC, Petrie J. Liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (LEADER™) trial: rationale and study design. Diabetic Medicine 2012;29:68. [EMBASE: 70695949]
-
- Bergenstal R, Daniels G, Mann J, Nissen S, Pocock S, Zinman B, et al. Liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (LEADER™) trial: Rationale and study design. Diabetes 2011;60:A612-3. [EMBASE: 70630008]
-
- Consoli A, Bergenstal R, Daniels G, Mann J, Nissen S, Pocock S, et al. Liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (leader) trial: Rationale and study design. High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Prevention 2012;19(2):104. [EMBASE: 713987964]
-
- Mannucci E, Bergenstal R, Daniels G, Mann J, Nissen S, Zinman B, et al. Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome Results (LEADER) Trial: Rationale and study design. Italian Journal of Medicine 2012;6(1 Suppl 1):86. [EMBASE: 70799751]
-
- Marso SP, Poulter NR, Nissen SE, Nauck MA, Zinman B, Daniels GH, et al. Design of the liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (LEADER) trial. American Heart Journal 2013;166:823-30. [EMBASE: 2013691152] - PubMed
Le Roux 2018 {published data only}
Lewis 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lewis K. Weight loss achieved with medication can delay onset of type 2 diabetes in at-risk individuals. Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management 2014;21:393-5. [EMBASE: 2014910274]
Lindgarde 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lindgarde F. The effect of orlistat on body weight and coronary heart disease risk profile in obese patients: the Swedish Multimorbidity Study [see comment]. Journal of Internal Medicine 2000;248(3):245-54. - PubMed
Lindgarde 2001a {published data only}
-
- Lindgarde F. Orlistat with diet was effective and safe for weight loss and coronary risk reduction in obesity. Evidence-based Medicine 2001;6(2):54.
Lindgarde 2001b {published data only}
-
- Lindgarde F. Effect of orlistat on coronary heart disease risk in obese patients with hypertension and/or hyperlipidemia. American Heart Journal 2001;141(1):171.
Lu 2018 {published data only}
-
- Lu CW, Chang CJ, Yang YC, Lin WY, Huang KC. Multicentre, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight management in Chinese population. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice 2018;12(5):465-71. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Madsen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Madsen EL, Bruun JM, Skogstrand K, Hougaard DM, Christiansen T, Richelsen B. Long-term weight loss decreases the nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors interleukin-18 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in obese subjects. Metabolism 2009;58(7):946-53. - PubMed
McMahon 2000 {published data only}
-
- McMahon FG, Fujioka K, Singh BN, Mendel CM, Rowe E, Rolston K, et al. Efficacy and safety of sibutramine in obese white and African American patients with hypertension: a 1-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160(14):2185-91. [PMID: ] - PubMed
McMahon 2002 {published data only}
-
- McMahon FG, Weinstein SP, Rowe E, Ernst KR, Johnson F, Fujioka K, et al. Sibutramine is safe and effective for weight loss in obese patients whose hypertension is well controlled with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Journal of Human Hypertension 2002;16(1):5-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
McNulty 2003 {published data only}
-
- McNulty SJ, Ur E, Williams G, Multicenter Sibutramine Study Group. A randomized trial of sibutramine in the management of obese type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin. Diabetes Care 2003;26(1):125-31. - PubMed
Miles 2002 {published data only}
-
- Miles JM, Leiter L, Hollander P, Wadden T, Anderson JW, Doyle M, et al. Effect of orlistat in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin [erratum appears in Diabetes Care 2002 Sep;25(9):1671]. Diabetes Care 2002;25(7):1123-8. - PubMed
Moore 2016 {published data only}
-
- Moore KG, Shealy K, Clements JN. Liraglutide, GLP-1 receptor agonist, for chronic weight loss. Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism 2016;11(5):373-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
NCT01764386 {published data only}
-
- NCT01764386. A multicenter, randomized, open-label, controlled, method-of-use study assessing the effect of naltrexone sustained release (SR)/bupropion SR on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese subjects (The Ignite Study). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01764386 (first received 09 January 2013).
Niskanen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Niskanen L, Astrup A, Hakim MA, Carraro R, Finer N, Hartvig H, et al. Liraglutide once daily reduces the prevalence of prediabetes and metabolic syndrome in obese non-diabetic adults: a 2-year randomized trial. Obesity 2010;18:S56. [EMBASE: 71774529]
Nissen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nissen SE, Nicholls SJ, Wolski K, Rodes-Cabau J, Cannon CP, Deanfield JE, et al. Effect of rimonabant on progression of atherosclerosis in patients with abdominal obesity and coronary artery disease: the STRADIVARIUS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008;299(13):1547-60. - PubMed
O'Leary 2011 {published data only}
-
- O'Leary DH, Reuwer AQ, Nissen SE, Despres JP, Deanfield JE, Brown MW, et al. Effect of rimonabant on carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) progression in patients with abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome: the AUDITOR Trial. Heart 2011;97(14):1143-50. - PubMed
Pathan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pathan MF, Latif ZA, Nazneen NE, Mili SU. Orlistat as an adjunct therapy in type 2 obese diabetic patients treated with sulphonylurea: a Bangladesh experience. Bangladesh Medical Research Council Bulletin 2004;30(1):1-8. - PubMed
Patschan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Patschan S, Scholze J. Obesity-related hypertension. Cardiology Review 2007;24(12):32-5.
Pi‐Sunyer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, Devin J, Rosenstock J, RIO-North America Study Group. Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial [see comment] [erratum appears in JAMA 2006 Mar 15;295(11):1252]. JAMA 2006;295(7):761-75. - PubMed
Reaven 2001 {published data only}
-
- Reaven G, Segal K, Hauptman J, Boldrin M, Lucas C. Effect of orlistat-assisted weight loss in decreasing coronary heart disease risk in patients with syndrome X. American Journal of Cardiology 2001;87(7):827-31. - PubMed
Rossner 2000 {published data only}
-
- Rossner S, Sjöström L, Noack R, Meinders AE, Noseda G. Weight loss, weight maintenance, and improved cardiovascular risk factors after 2 years treatment with orlistat for obesity. European Orlistat Obesity Study Group. Obesity Research 2000;8(1):49-61. - PubMed
Rossner 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rossner S. Sibutramine - antidepressive agent tested against obesity [Sibutramin – antidepressivt läkemedel prövat mot fetma]. Lakartidningen 2001;98(15):1802-3. - PubMed
Samuelsson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Samuelsson L, Gottsater A, Lindgarde F. Decreasing levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 during lowering of body mass index with orlistat or placebo in obese subjects with cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2003;5(3):195-201. - PubMed
SCALE diabetes 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bode B, DeFronzo R, Bergenstal R, Kushner R, Lewin A, Skjoth TV, et al. Effect of liraglutide 3.0/1.8 mg on body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight/obese adults with type 2 diabetes: SCALE diabetes randomised, double-blind, 56-week trial. Diabetologia 2014;57(Suppl 1):S83. [EMBASE: 71594831]
-
- Davies MJ, DeFronzo RA, Bergenstal RM, Bode BW, Kushner R, Noctor M, et al. Liraglutide 3.0mg results in significant weight loss and improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors compared with liraglutide 1.8mg or placebo: a randomised, double-blind, 56 week trial in overweight/obese adults with Type 2 diabetes (SCALE diabetes). Diabetic Medicine 2015;32:72. [EMBASE: 71821008]
-
- DeFronzo RA, Bergenstal RM, Bode B, Kushner R, Lewin AJ, Skjoth TV, et al. Effects of liraglutide 3.0 mg and 1.8 mg on body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): the SCALE diabetes randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 56-week trial. Endocrine Reviews 2014;35:var. [EMBASE: 4344566]
-
- Pedersen S, Defronzo RA, Bergenstal R, Bode B, Kushner R, Lewin A, et al. Effects of liraglutide 3.0 mg and 1.8 mg on body weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D): The SCALE diabetes randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 56-week trial. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2015;39:S36. [EMBASE: 1860363]
SCALE maintenance 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hollander P, Aronne L, Klein S, Niswender K, Jensen CB, Woo V, et al. Diet-induced weight loss and subsequent addition of liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces impaired fasting glucose in overweight/obese adults in the SCALE™ maintenance 56-week randomised trial. Journal of Diabetes 2013;5:124. [EMBASE: 71034943]
-
- Klein S, Aronne LJ, Hollander P, Niswender K, Woo V, Hale PM, et al. Effect of liraglutide on cardiovascular (CV) risk factors in adults without diabetes after diet-induced weight loss: the SCALE 56-week randomized study. Obesity 2011;19:S177.
SCALE obesity and prediabetes 2014 {published data only}
-
- Astrup A, Fujioka K, Violante Ortiz R, Jensen CB, Lillerre SK, O'Neil P. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide 3.0 mg in adult overweight and obese weight loss responders without diabetes: results of the 56-week randomised, controlled, SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial. Obesity Facts 2015;8(Suppl 1):42. [EMBASE: 71907401]
-
- Astrup A, Greenway F, Krempf M, Le Roux CW, Vettor R, Shapiro Manning L, et al. Weight loss and associated improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors with liraglutide 3.0 mg in the SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled 3-year trial. Obesity Facts 2016;9(Suppl 1):182. [EMBASE: 72316004]
-
- Bjorner JB, Brett JH, Meincke HH, Kolotkin RL. The effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg for weight management on hrqol, as measured by SF-36: 3-year data. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S330. [EMBASE: 612314178]
-
- Fujioka K, Greenway FL, Krempf M, Le Roux CW, Vettor R, Manning LS, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces body weight and improves cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with obesity or overweight and prediabetes: the SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 3-year trial. Endocrine Reviews 2016;37(2 Suppl 1):no pagination. [EMBASE: 613520086]
-
- Fujioka K, Wilding JP, Astrup A, Greenway F, Halpern A, Krempf M, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide 3.0 mg for weight management in overweight/obese adults: The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial. Diabetologia 2014;57(Suppl1):S368-9. [EMBASE: 71595554]
SCALE sleep apnoea 2014 {published data only}
-
- Blackman A, Foster G, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Aronne L, Wadden T, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces severity of obstructive sleep apnea and body weight in obese individuals with moderate or severe disease: SCALE sleep apnoea tria. Sleep Medicine 2015;16(Suppl 1):S24. [EMBASE: 4282911]
-
- Blackman A, Foster G, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Aronne L, Wadden T, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces severity of obstructive sleep apnoea and body weight in obese individuals with moderate or severe disease: SCALE sleep apnoea trial. Diabetologia 2014;57(1 Suppl 1):S85. [EMBASE: 1745360]
-
- Blackman A, Foster G, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Wadden T, Aronne L, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces severity of obstructive sleep apnea and body weight in individuals with obesity and moderate or severe disease: SCALE sleep apnoea trial. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2015;39(Suppl 1):S35. [EMBASE: 1826652]
-
- Blackman A, Foster GD, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Aronne L, Wadden T, et al. Effect of liraglutide 3.0mg in individuals with obesity and moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea: the SCALE sleep apnea randomized clinical trial. International Journal of Obesity 2016;40(8):1310-9. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collier A, Blackman A, Foster G, Zammit G, Rosenberg R, Wadden T, et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg reduces severity of obstructive sleep apnoea and body weight in obese individuals with moderate or severe disease: SCALE sleep apnoea trial. Thorax 2014;69(Suppl 2):A16-7. [EMBASE: 71688686]
Scheen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Scheen AJ, Ernest P. New antiobesity agents in type 2 diabetes: Overview of clinical trials with sibutramine and orlistat. Diabetes and Metabolism 2002;28(6 I):437-45. - PubMed
Scott 2015 {published data only}
-
- Scott LJ. Liraglutide: a review of its use in the management of obesity. Drugs 2015;75(8):899-910. [PMID: ] - PubMed
SCOUT 2010 {published data only}
-
- James P, Caterson I, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal L, Maggioni A, et al. Effects on mortality and morbidity in overweight/obese subjects: the sibutramine cardiovascular outcomes (SCOUT) trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2010;Conference: American College of Cardiology's 59th Annual Scientific Session and i2 Summit: Innovation in Intervention Atlanta, GA United States. Conference Start: 20100314 Conference End: 20100316. Conference Publication:(var.pagings). 55 (10 SUPPL 1):A141.E1326.
-
- James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, et al. Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(10):905-17. - PubMed
-
- Kamil S, Finer N, James WP, Caterson ID, Andersson C, Torp-Pedersen C. Influence of sibutramine in addition to diet and exercise on the relationship between weight loss and blood glucose changes. European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy 2017;3(3):134-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Maggioni AP, Caterson I, Coutinho W, Finer N, Gaal LV, Sharma AM, et al. Tolerability of sibutramine during a 6-week treatment period in high-risk patients with cardiovascular disease and/or diabetes: a preliminary analysis of the Sibutramine Cardiovascular Outcomes (SCOUT) Trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2008;52(5):393-402. - PubMed
-
- Seimon R, Espinoza D, Ivers L, Gebski V, Finer N, Legler U, et al. Changes in body weight and blood pressure: Paradoxical outcome events in overweight and obese subjects with cardiovascular disease. Obesity Reviews 2014;15:173. [EMBASE: 71516191] - PubMed
SEQUEL 2014 {published data only}
-
- Garvey WT, Najarian T, Peterson CA. Significant weight loss with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate (PHEN/TPM CR) is associated with significant reductions in use of concomitant medications for cardiometabolic diseases over 108 weeks. Obesity 2011;19:S176. [EMBASE: 70680319]
-
- Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, Gadde KM, Allison DB, Peterson CA, et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2012;95:297-308. [EMBASE: 2012064424] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klein S, Najarian T, Troupin B, Day WW. Weight loss (WL) with low-dose, controlled-release phentermine/topiramate (PHEN/TPM CR) correlates with improvements in liver function in overweight/obese adults with elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Obesity 2011;19:S177. [EMBASE: 70680321]
-
- Toplak H, Rossner S, Garvey WT, Troupin B, Bowden CH. Long-term weight loss with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate reverses metabolic syndrome and improves associated traits. Diabetologia 2011;54:S370. [EMBASE: 70563050]
Sharif 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sharif Z, Peikanpour M, Rangchian M, Foroughi Moghadam MJ. Cost-utility analysis of lorcaserin in the treatment of obesity. Value in Health 2017;7:A590-A591. [EMBASE: 613234809]
Shaw Tronieri 2018 {published data only}
-
- Shaw Tronieri J, Wadden TA, Berkowitz RI, Chao AM, Pearl RL, Alamuddin N, et al. A randomized trial of lorcaserin and lifestyle counseling for maintaining weight loss achieved with a low-calorie diet. Obesity 2018;26(2):299-309. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sjöström 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, Boldrin M, Golay A, Koppeschaar HP, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group [see comment]. Lancet 1998;352(9123):167-72. - PubMed
Starling 2001 {published data only}
-
- Starling RD, Liu X, Sullivan DH. Influence of sibutramine on energy expenditure in African American women. Obesity Research 2001;9(4):251-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Strebkova 2015 {published data only}
-
- Strebkova E, Solovyova I, Sharapova E, Mkrtumyan A, Alekseeva L, Nasonov E. Impact of body weight loss on the clinical manifestations of knee osteoarthritis and metabolic syndrome parameters in female patients with obesity taking orlistat. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2015;74:1183-4. [EMBASE: 4338732]
Suyog 2011 {published data only}
-
- Suyog J, Milind P, Karuna R. Comparison of efficacy and safety of rimonabant with orlistat in obese and overweight patients. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences 2011;2(1):179-87.
Svendsen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Svendsen M, Rissanen A, Richelsen B, Rossner S, Hansson F, Tonstad S. Effect of orlistat on eating behavior among participants in a 3-year weight maintenance trial. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(2):327-33. - PubMed
Swinburn 2005 {published data only}
-
- Swinburn BA, Carey D, Hills AP, Hooper M, Marks S, Proietto J, et al. Effect of orlistat on cardiovascular disease risk in obese adults. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2005;7(3):254-62. - PubMed
Tambascia 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tambascia MA, Geloneze B, Repetto EM, Geloneze SR, Picolo M, Magro DO. Sibutramine enhances insulin sensitivity ameliorating metabolic parameters in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2003;5(5):338-44. - PubMed
Tiikkainen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tiikkainen M, Bergholm R, Rissanen A, Aro A, Salminen I, Tamminen M, et al. Effects of equal weight loss with orlistat and placebo on body fat and serum fatty acid composition and insulin resistance in obese women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004;79(1):22-30. - PubMed
Triay 2012 {published data only}
Tunyan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Tunyan AM. Cardioprotective effects of antihypertensive therapy with orlistat treatment and hypocaloric diet in combination in obese hypertensive patients. Circulation 2007;115(8):E248. [CENTRAL: CN-00868400]
Van Gaal 2005 {published data only}
-
- Van Gaal LF, Rissanen AM, Scheen AJ, Ziegler O, Rossner S, RIO-Europe Study Group. Effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker rimonabant on weight reduction and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight patients: 1-year experience from the RIO-Europe study [see comment] [erratum appears in Lancet 2005 Jul 30-Aug 5;366(9483):370]. Lancet 2005;365(9468):1389-97. - PubMed
Van Gaal 2008 {published data only}
-
- Van Gaal LF, Scheen AJ, Rissanen AM, Rossner S, Hanotin C, Ziegler O, et al. Long-term effect of CB1 blockade with rimonabant on cardiometabolic risk factors: two year results from the RIO-Europe Study. European Heart Journal 2008;29(14):1761-71. - PubMed
Von Scholten 2015 {published data only}
-
- Von Scholten BJ, Hansen TW, Goetze JP, Persson F, Rossing P. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA): long-term effect on kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications 2015;29(5):670-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Wang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wang YJ, Liu C, Liu YM. Orlistat for adjuvant treatment of fatty type 2 diabetes mellitus in 32 patients. Zhongguo Xin Yao Yu Lin Chuang Za Zhi [Chinese journal of new drugs and clinical remedies] 2003;22(11):651-3.
Winslow 2012 {published data only}
-
- Winslow DH, Bowden CH, DiDonato K, McCullough PA. The effects of once-daily 15mg phentermine plus 92mg topiramate extended-release (PHEN/TPM ER) on cardiometabolic endpoints in obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2013;36:A297. [EMBASE: 71513682]
Wirth 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wirth A, Krause J. Long-term weight loss with sibutramine: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001;286(11):1331-9. - PubMed
Ye 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ye J, Yanqin W, Xuan H, Bihui Z. Effect of orlistat on total liver fat quantification by novel magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: interim analysis of a prospective, randomized, single-center, open-label trial. United European Gastroenterology Journal 2017;5(Supplement 1):A625. [EMBASE: 7471868]
Zannad 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zannad F, Gille B, Grentzinger A, Bruntz JF, Hammadi M, Boivin JM, et al. Effects of sibutramine on ventricular dimensions and heart valves in obese patients during weight reduction. American Heart Journal 2002;144(3):508-15. - PubMed
Zavoral 1998 {published data only}
-
- Zavoral JH. Treatment with orlistat reduces cardiovascular risk in obese patients. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16(12 Pt 2):2013-7. - PubMed
Additional references
Abbott 2010
-
- Abbott Germany Theobald F. Press release: [Abbott setzt Vertrieb seiner Medikamente mit dem Wirkstoff Sibutramin zur Behandlung von Adipositas in den Ländern der Europäischen Union aus.] 2010. Available from: www.abbott.de/press/show/e7340/e19695/e18095/Sibutramin_210110_Theobald_... (cited 14 January 2013).
ACC/AHA 2017
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.. Hypertension 2018;71(6):1269-1324. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Apovian 2015
-
- Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, McDonnell ME, Murad MH, Pagotto U, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2015;100(2):342-62. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Aronne 2013
-
- Aronne LJ, Wadden TA, Peterson C, Winslow D, Odeh S, Gadde KM. Evaluation of phentermine and topiramate versus phentermine/topiramate extended-release in obese adults. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 2013;21(11):2163-71. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Aucott 2005
-
- Aucott L, Poobalan A, Smith WC, Avenell A, Jung R, Broom J. Effects of weight loss in overweight/obese individuals and long-term hypertension outcomes: a systematic review. Hypertension 2005;45(6):1035-41. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Caixas 2014
Chan 2013
-
- Chan EW, He Y, Chui CS, Wong AY, Lau WC, Wong IC. Efficacy and safety of lorcaserin in obese adults: a meta-analysis of 1-year randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and narrative review on short-term RCTs. Obesity Reviews: an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 2013;14(5):383-92. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Corbett 2014
-
- Corbett MS, Higgins JP, Woolacott NF. Assessing baseline imbalance in randomised trials: implications for the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Research Synthesis Methods 2014;5:79-85. [PMID: ] - PubMed
CRESCENDO 2010
-
- Topol EJ, Bousser MG, Fox KA, Creager MA, Despres JP, Easton JD, et al. Rimonabant for prevention of cardiovascular events (CRESCENDO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376(9740):517-23. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Deeks 2019
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Derosa 2005
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Murdolo G, Piccinni MN, Fogari E, Bertone G, et al. Efficacy and safety comparative evaluation of orlistat and sibutramine treatment in hypertensive obese patients. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2005;7(1):47-55. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Eisai Inc. 2020
-
- Eisai Incorporation. Eisai to Voluntarily Withdraw BELVIQ®/BELVIQ XR® in the U.S.. Available from: eisai.mediaroom.com/2020-02-13-Eisai-to-Voluntarily-Withdraw-BELVIQ-R-BE... (13 February 2020; cited 30 March 2020).
EMA 2008a
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Questions and answers on the recommendation to suspend the marketing authorisation of Acomplia (rimonabant). Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Medicine_QA/2009/11/WC5000... (updated 23 October 2008; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2008b
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Press Release - The European Medicines Agency recommends suspension of the marketing authorisation of Acomplia. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Press_release/2009/11/WC50... (updated 23 October 2008; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2009a
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Public Statement on Acomplia (rimonabant) - Withdrawal of the marketing authorisation in the European Union. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Public_statement/2009/11/W... (updated 30 January 2009; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2009b
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Victoza (liraglutide) - EPAR - Summary for the public. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Summary_for_the_pub... (updated 8 July 2009; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2010a
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Press Release - European Medicines Agency recommends suspension of marketing authorisations for sibutramine. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Press_release/2010/01/WC50... (updated 21 January 2010; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2010b
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Questions and answers on the suspension of medicines containing sibutramine. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Referrals_document/Sibutra... (updated 6 August 2010; cited 17 December 2012).
EMA 2013a
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Questions and answers on the withdrawal of the marketing authorisation application for Belviq (lorcaserin). Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Medicine_QA/2013/05/WC5001... (updated 31 May 2013; cited 20 July 2015).
EMA 2013b
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Withdrawal assessment report for Belviq. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Application_withdrawal_ass... (updated 20 August 2013; cited 20 July 2015).
EMA 2013c
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Questions and answers on the refusal of the marketing authorisation for Qsiva (phentermine/topiramate). Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Summary_of_opinion_-_Initi... (updated 22 February 2013; cited 20 July 2015).
EMA 2013d
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Scientific conclusions and grounds for refusal of the marketing authorisation for Qsiva (13 June 2013). Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medicines/002... (updated 13 June 2013; cited 20 July 2015).
EMA 2015a
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Mysimba (naltrexone/bupropion) - EPAR summary for the public. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Summary_for_the_pub... (updated 15 April 2015; cited 20 July 2015).
EMA 2015b
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Saxenda (liraglutide) - EPAR summary for the public. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Summary_for_the_pub... (updated 16 April 2015; cited 20 July 2015).
ESC/ESH 2018
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. European Heart Journal 2018;39(33):3021-3104. [PMID: ] - PubMed
FDA 2007
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Egan AG, Colman EG. FDA Rimonabant Briefing Document. Endocrine and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee. 2007. Available from: https://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170405052424/https://www.fda.gov/o... (updated 13 June 2007; cited 18 December 2012).
FDA 2010a
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Recommendation on a regulatory decision for Meridia (sibutramine). http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170113112219/http:/www.fda.gov/down... (updated 7 October 2010; cited 18 December 2012).
FDA 2010b
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA News Release: Abbott Laboratories agrees to withdraw its obesity drug Meridia. http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170112215610/http:/www.fda.gov/News... (updated 8 October 2010; cited 18 December 2012).
FDA 2010c
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Victoza (Liraglutide (rDNA)) - Approval letter. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2010/022341s000TOC.cfm (updated 25 January 2010; cited 20 July 2015).
FDA 2012a
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Qsymia (phentermine and topiramate extended-release) - Approval letter. Available from: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2012/022580Orig1s000Approv.pdf (updated 17 July 2012; cited 20 July 2015).
FDA 2012b
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Belviq (lorcaserin hydrochloride) - Approval letter. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2012/022529Orig... (updated 27 June 2012; cited 20 July 2015).
FDA 2014a
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Contrave (naltrexone hydrochloride/bupropion hydrochloride) - Approval letter. Available from: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/200063Orig1s000Approv.pdf (updated 10 September 2014; cited 20 July 2015).
FDA 2014b
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Saxenda (liraglutide) - Approval letter. Available from: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2014/206321Orig1s000ltr... (updated 23 December 2014; cited 20 July 2015).
FDA 2020
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug Safety Communication - FDA requests the withdrawal of the weight-loss drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the market. Available from: www.fda.gov/media/135189/download (updated 13 February 2020; cited 30 March 2020).
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383-94. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Handbook 2019
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2019. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Higgins 2019
-
- Higgins JP, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Sterne JA. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Horvath 2008
-
- Horvath K, Jeitler K, Siering U, Stich AK, Skipka G, Gratzer TW, et al. Long-term effects of weight-reducing interventions in hypertensive patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168(6):571-80. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hróbjartsson 2013
-
- Hróbjartsson A, Thomsen AS, Emanuelsson F, Tendal B, Hilden J, Boutron I et al. Observer bias in randomized clinical trials with measurement scale outcomes: a systematic review of trials with both blinded and nonblinded assessors. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(4):E201-11. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Hypertension Canada 2018
-
- Nerenberg KA, Zarnke KB, Leung AA, Dasgupta K, Butalia S, McBrien K, et al. Hypertension Canada's 2018 Guidelines for diagnosis, risk assessment, prevention, and treatment of hypertension in adults and children. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2018;34(5):506-25. [PMID: ] - PubMed
IQWiG 2006
-
- Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (IQWiG). Evaluation of the benefits and harms of non-drug weight-reducing treatment strategies in patients with essential hypertension [Nutzenbewertung nichtmedikamentöser Behandlungsstrategien bei Patienten mit Bluthochdruck: A-Gewichtsreduktion]. Available from: iqwig.de/download/A05-21A_Abschlussbericht_Gewichtsreduktion_bei_Bluthoc... 2006:19-119.
Kim 2003
-
- Kim SH, Lee YM, Jee SH, Nam CM. Effect of sibutramine on weight loss and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of controlled trials. Obesity Research 2003;11(9):1116-23. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lefebvre 2019
-
- Lefebvre C, Glanville J, Briscoe S, Littlewood A, Marshall C, Metzendorf M-I, et al. Chapter 4: Searching for and selecting studies. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
NEJM Journal Watch 2011
-
- NEJM Journal Watch. FDA reminds clinicians of liraglutide’s risks for pancreatitis and cancer. Available from: www.jwatch.org/fw201106140000002/2011/06/14/fda-reminds-clinicians-lirag... (cited 20 July 2015).
NICE 2019
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management (NG136). Available from: //www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng136 (last updated 28 August 2019; cited 3 April 2020).
Padwal 2007
-
- Padwal RS, Majumdar SR. Drug treatments for obesity: orlistat, sibutramine, and rimonabant. Lancet 2007;369(9555):71-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
PRISMA 2009
-
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151(4):264-9, W64. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Russell‐Jones 2009
-
- Russell-Jones D. Molecular, pharmacological and clinical aspects of liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analogue. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2009;297(1-2):137-40. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Scheen 2006
-
- Scheen AJ, Finer N, Hollander P, Jensen MD, Van Gaal LF. Efficacy and tolerability of rimonabant in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled study. Lancet 2006;368(9548):1660-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Shyangdan 2011
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Taylor 2013
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Day 2013 – A global brief on hypertension. 2013. Available from: www.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/79059/1/WHO_DCO_WHD_2013.2_eng.pdf (cited 20 July 2015).
References to other published versions of this review
Siebenhofer 2009
Siebenhofer 2009a
Siebenhofer 2013
Siebenhofer 2016
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

