Immediate response to apremilast in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis: a retrospective pilot study
- PMID: 33454961
- PMCID: PMC8248100
- DOI: 10.1111/ijd.15382
Immediate response to apremilast in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis: a retrospective pilot study
Abstract
Background: Recent case reports have shown the efficacy of apremilast for the treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP). However, no study has statistically analyzed the clinical efficacy of oral apremilast in patients with PPP.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of apremilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, for PPP.
Materials and methods: Among 13 patients who were diagnosed with PPP, 10 patients with PPP with either palmoplantar pustules (>1 mm diameter) or sternoclavicular joint pain were retrospectively analyzed.
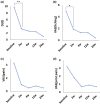
Results: Palmoplantar Pustulosis Area and Severity Index (mean ± SD: baseline, 13.4 ± 9.5 vs. after treatment, 5.1 ± 5.6; P = 0.013) and the number of pustules measuring > 1 mm in diameter (3.9 ± 3.9 vs. 1.3 ± 1.9; P = 0.029) significantly improved in 2 (±1) weeks. Moreover, the Dermatology Life Quality Index (9.7 ± 7.0 vs. 3.3 ± 3.6; P = 0.009) and palmoplantar itching (visual analog scale [VAS] score) (5.6 ± 3.5 vs. 2.1 ± 2.2; P = 0.026) significantly improved in 2 weeks, whereas VAS scores of palmoplantar pain (4.8 ± 4.4 vs. 1.1 ± 2.4; P = 0.081) and sternoclavicular joint pain (3.2 ± 3.8 vs. 2.0 ± 2.6; P = 0.194) did not significantly improve. Diarrhea was observed in 60.0% of our patients.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that apremilast can effectively treat cutaneous manifestations and arthralgia in Japanese patients with PPP who had apparent pustules and/or clavicular-sternocostal arthralgia. Owing to the retrospective design of the study and a small sample size, placebo-controlled clinical trials with a larger number of patients are warranted to confirm the efficacy of apremilast for treatment of PPP.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the International Society of Dermatology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Apremilast for the Treatment of Japanese Patients with Palmoplantar Pustulosis: Results from a Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Sep;24(5):837-847. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00788-2. Epub 2023 May 26. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37233897 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A multicentre open-label study of apremilast in palmoplantar pustulosis (APLANTUS).J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021 Oct;35(10):2045-2050. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17441. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021. PMID: 34077577 Clinical Trial.
-
Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, in the treatment of palmoplantar psoriasis: Results of a pooled analysis from phase II PSOR-005 and phase III Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis (ESTEEM) clinical trials in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Jul;75(1):99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1164. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27021239 Clinical Trial.
-
Apremilast in Palmoplantar Psoriasis and Palmoplantar Pustulosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Feb;13(2):437-451. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00877-w. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 36609960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apremilast: A Review in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.Drugs. 2017 Mar;77(4):459-472. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0709-1. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28213862 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in palmoplantar pustulosis.Fac Rev. 2021 Jul 27;10:62. doi: 10.12703/r/10-62. eCollection 2021. Fac Rev. 2021. PMID: 34409425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health-related quality of life in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis - a Swedish register study.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2386524. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2386524. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39115530 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Therapies for Palmoplantar Pustulosis with a Focus on IL-23 Inhibitors.J Clin Med. 2025 May 8;14(10):3273. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103273. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Apremilast for the Treatment of Japanese Patients with Palmoplantar Pustulosis: Results from a Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Sep;24(5):837-847. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00788-2. Epub 2023 May 26. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37233897 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Involvement of Molecular Mechanisms between T/B Cells and IL-23: From Palmoplantar Pustulosis to Autoimmune Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 27;23(15):8261. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158261. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Griffiths CE, Christophers E, Barker JN, et al. A classification of psoriasis vulgaris according to phenotype. Br J Dermatol 2007; 156: 258–262. - PubMed
-
- Kati A, Mahreen A, Sari S, et al. Genetic analysis of PSORS1 distinguishes guttate psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 120: 627–632. - PubMed
-
- Huang CM, Tsai TF. Clinical characteristics, genetics, comorbidities and treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis: A retrospective analysis of 66 cases in a single center in Taiwan. J Dermatol 2020; 47(9): 1046–1049 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with palmoplantar pustulosis. Clin Drug Investig 2019; 39: 241–252. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

