Immediate response to apremilast in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis: a retrospective pilot study
- PMID: 33454961
- PMCID: PMC8248100
- DOI: 10.1111/ijd.15382
Immediate response to apremilast in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis: a retrospective pilot study
Abstract
Background: Recent case reports have shown the efficacy of apremilast for the treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP). However, no study has statistically analyzed the clinical efficacy of oral apremilast in patients with PPP.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of apremilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, for PPP.
Materials and methods: Among 13 patients who were diagnosed with PPP, 10 patients with PPP with either palmoplantar pustules (>1 mm diameter) or sternoclavicular joint pain were retrospectively analyzed.
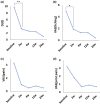
Results: Palmoplantar Pustulosis Area and Severity Index (mean ± SD: baseline, 13.4 ± 9.5 vs. after treatment, 5.1 ± 5.6; P = 0.013) and the number of pustules measuring > 1 mm in diameter (3.9 ± 3.9 vs. 1.3 ± 1.9; P = 0.029) significantly improved in 2 (±1) weeks. Moreover, the Dermatology Life Quality Index (9.7 ± 7.0 vs. 3.3 ± 3.6; P = 0.009) and palmoplantar itching (visual analog scale [VAS] score) (5.6 ± 3.5 vs. 2.1 ± 2.2; P = 0.026) significantly improved in 2 weeks, whereas VAS scores of palmoplantar pain (4.8 ± 4.4 vs. 1.1 ± 2.4; P = 0.081) and sternoclavicular joint pain (3.2 ± 3.8 vs. 2.0 ± 2.6; P = 0.194) did not significantly improve. Diarrhea was observed in 60.0% of our patients.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that apremilast can effectively treat cutaneous manifestations and arthralgia in Japanese patients with PPP who had apparent pustules and/or clavicular-sternocostal arthralgia. Owing to the retrospective design of the study and a small sample size, placebo-controlled clinical trials with a larger number of patients are warranted to confirm the efficacy of apremilast for treatment of PPP.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the International Society of Dermatology.
Figures



References
-
- Griffiths CE, Christophers E, Barker JN, et al. A classification of psoriasis vulgaris according to phenotype. Br J Dermatol 2007; 156: 258–262. - PubMed
-
- Kati A, Mahreen A, Sari S, et al. Genetic analysis of PSORS1 distinguishes guttate psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 120: 627–632. - PubMed
-
- Huang CM, Tsai TF. Clinical characteristics, genetics, comorbidities and treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis: A retrospective analysis of 66 cases in a single center in Taiwan. J Dermatol 2020; 47(9): 1046–1049 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with palmoplantar pustulosis. Clin Drug Investig 2019; 39: 241–252. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

