Gap Junction Liposomes for Efficient Delivery of Chemotherapeutics to Solid Tumors
- PMID: 33455217
- PMCID: PMC8483596
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01047
Gap Junction Liposomes for Efficient Delivery of Chemotherapeutics to Solid Tumors
Abstract
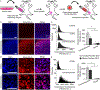
Chemotherapeutic delivery is limited by inefficient transport across cellular membranes. Here, we harness the cellular gap junction network to release therapeutic cargos directly into the cytosol. Specifically, cell-derived vesicles, termed connectosomes, contain gap junction transmembrane proteins that open a direct passageway to the cellular interior. Connectosomes were previously shown to substantially improve chemotherapeutic delivery in vitro. Here, we test connectosomes in vivo, using a murine breast tumor model. We demonstrate that connectosomes improve chemotherapeutic delivery to cellular targets within tumors by up to 16-fold, compared to conventional drug-loaded liposomes, suggesting an efficient alternative pathway for intracellular delivery.
Keywords: delivery; gap junction channels; intracellular; intratumoral; murine mammary tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barenholz Y, Doxil(R)--the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J Control Release 2012, 160 (2), 117–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
