Forest and Trees: Exploring Bacterial Virulence with Genome-wide Association Studies and Machine Learning
- PMID: 33455849
- PMCID: PMC8187264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.12.002
Forest and Trees: Exploring Bacterial Virulence with Genome-wide Association Studies and Machine Learning
Abstract
The advent of inexpensive and rapid sequencing technologies has allowed bacterial whole-genome sequences to be generated at an unprecedented pace. This wealth of information has revealed an unanticipated degree of strain-to-strain genetic diversity within many bacterial species. Awareness of this genetic heterogeneity has corresponded with a greater appreciation of intraspecies variation in virulence. A number of comparative genomic strategies have been developed to link these genotypic and pathogenic differences with the aim of discovering novel virulence factors. Here, we review recent advances in comparative genomic approaches to identify bacterial virulence determinants, with a focus on genome-wide association studies and machine learning.
Keywords: bacteria; genomics; virulence.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
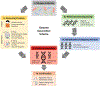
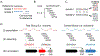

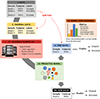
References
-
- Fleischmann RD, et al. (1995) Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 269, 496–512 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

