Inhibition of COX-2 Impairs Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis through Reduced Stromal Cell Reaction
- PMID: 33455946
- PMCID: PMC8094073
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.160
Inhibition of COX-2 Impairs Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis through Reduced Stromal Cell Reaction
Abstract
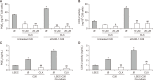
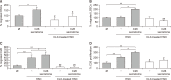
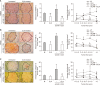
Liver colonization is initiated through the interplay between tumor cells and adhesion molecules present in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs). This crosstalk stimulates tumor COX-2 upregulation and PGE2 secretion. To elucidate the role of the LSEC intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the prometastatic response exerted by tumor and stromal COX-2, we utilized celecoxib (CLX) as a COX-2 inhibitory agent. We analyzed the in vitro proliferative and secretory responses of murine C26 colorectal cancer (CRC) cells to soluble ICAM-1 (sICAM-1), cultured alone or with LSECs, and their effect on LSEC and hepatic stellate cell (HSC) migration and in vivo liver metastasis. CLX reduced sICAM-1-stimulated COX-2 activation and PGE2 secretion in C26 cells cultured alone or cocultured with LSECs. Moreover, CLX abrogated sICAM-1-induced C26 cell proliferation and C26 secretion of promigratory factors for LSECs and HSCs. Interestingly, CLX reduced the protumoral response of HSC, reducing their migratory potential when stimulated with C26 secretomes and impairing their secretion of chemotactic factors for LSECs and C26 cells and proliferative factors for C26 cells. In vivo, CLX abrogated the prometastatic ability of sICAM-1-activated C26 cells while reducing liver metastasis. COX-2 inhibition blocked the creation of a favorable tumor microenvironment (TME) by hindering the intratumoral recruitment of activated HSCs and macrophages in addition to the accumulation of fibrillar collagen. These results point to COX-2 being a key modulator of processes initiated by host ICAM-1 during tumor cell/LSEC/HSC crosstalk, leading to the creation of a prometastatic TME in the liver.
Keywords: CAF; Colorectal cancer; Cyclooxygenase-2; Hepatic stellate cells; Liver metastasis; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
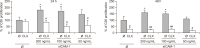



Similar articles
-
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell ICAM-1 mediated tumor/endothelial crosstalk drives the development of liver metastasis by initiating inflammatory and angiogenic responses.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 11;9(1):13111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49473-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31511625 Free PMC article.
-
Colon carcinoma cell interaction with liver sinusoidal endothelium inhibits organ-specific antitumor immunity through interleukin-1-induced mannose receptor in mice.Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2172-82. doi: 10.1002/hep.23590. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20513002
-
Silencing of sinusoidal DDR1 reduces murine liver metastasis by colon carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 27;10(1):18398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75395-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33110221 Free PMC article.
-
The role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in cancer liver metastasis.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 May 15;11(5):1845-1860. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34094657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver Microenvironment Response to Prostate Cancer Metastasis and Hormonal Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;14(24):6189. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246189. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin-1: A feasible link between liver pathologies and COVID-19.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 28;27(24):3516-3529. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i24.3516. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34239266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: The Origin, Biological Characteristics and Role in Cancer-A Glance on Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;14(18):4394. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184394. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Challenges of In Vitro CAF Modelling in Liver Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;13(23):5914. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235914. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Synthetic Analog of Resveratrol Inhibits the Proangiogenic Response of Liver Sinusoidal Cells during Hepatic Metastasis.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022 Mar 1;30(2):162-169. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.062. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 34873071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arteta B., Lasuen N., Lopategi A., Sveinbjörnsson B., Smedsrød B., Vidal-Vanaclocha F. Colon carcinoma cell interaction with liver sinusoidal endothelium inhibits organ-specific antitumor immunity through interleukin-1-induced mannose receptor in mice. Hepatology. 2010;51:2172–2182. doi: 10.1002/hep.23590. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benedicto A., Herrero A., Romayor I., Marquez J., Smedsrød B., Olaso E., Arteta B. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell ICAM-1 mediated tumor/endothelial crosstalk drives the development of liver metastasis by initiating inflammatory and angiogenic responses. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:13111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49473-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

