An Adult Case of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Successfully Treated with Balloon-occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration
- PMID: 33456037
- PMCID: PMC8263181
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5914-20
An Adult Case of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Successfully Treated with Balloon-occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration
Abstract
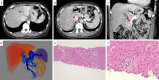
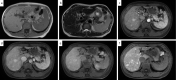
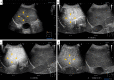
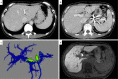
A 42-year-old woman visited our hospital due to syncope. Contrast-enhanced CT revealed portosystemic shunt, portal vein hypoplasia, and multiple liver nodules. The histological examination of a liver biopsy specimen exhibited portal vein hypoplasia and revealed that the liver tumor was positive for glutamine synthetase. The patient was therefore diagnosed with congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt type II, and with focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)-like nodules. She had the complication of severe portopulmonary hypertension and underwent complete shunt closure by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (B-RTO). The intrahepatic portal vein was well developed at 1 year after B-RTO, and multiple liver nodules completely regressed. Her pulmonary hypertension also improved.
Keywords: B-RTO; FNH-like nodule; congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt; portopulmonary hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Mistinova J, Valacsai F, Varga I. Congenital absence of the portal vein--Case report and a review of literature. Clin Anat 23: 750-758, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet 363: 1461-1468, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Ihara K, Hijii T, Kuromaru R, et al. . High-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted images in two toddlers with elevated blood manganese with portosystemic shunts. Neuroradiology 41: 195-198, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez AE, Ribeiro AF, Hessel G, Baracat J, Ribeiro JD. Abernethy malformation: one of the etiologies of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol 34: 391-394, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

