Statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy
- PMID: 33456195
- PMCID: PMC7785182
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1831298
Statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy
Abstract
Statins are the most widely used class of drug in the United States. They lower blood cholesterol levels by inhibiting 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Common side effects include myalgias and a mild increase in liver function tests. Statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy (SINAM) is a very rare side effect that is independent of the type and duration of statin use. Treatment involves high-dose steroids and immunosuppressants such as azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil. Nonresponders and patients with severe weakness can be treated with intravenous immunoglobulin or rituximab. We present a case of SINAM that was successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Keywords: Immunosuppressants; SINAM; rhabdomyolysis; statin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myopathy; statins.
Copyright © 2020 Baylor University Medical Center.
Figures
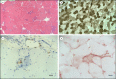
References
-
- Mach F, Ray KK, Wiklund O, et al; European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel . Adverse effects of statin therapy: perception vs. the evidence—focus on glucose homeostasis, cognitive, renal and hepatic function, haemorrhagic stroke and cataract. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(27):2526–2539. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehy182. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Troyanov Y, Landon-Cardinal O, Fritzler MJ, et al. . Atorvastatin-induced necrotizing autoimmune myositis: an emerging dominant entity in patients with autoimmune myositis presenting with a pure polymyositis phenotype. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(3):e5694. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000005694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
