Effect of lentivirus-mediated miR-182 targeting FGF9 on hallux valgus
- PMID: 33456347
- PMCID: PMC7807199
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.50984
Effect of lentivirus-mediated miR-182 targeting FGF9 on hallux valgus
Abstract
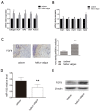
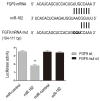
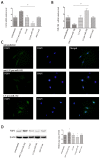
The pathogenesis of hallux valgus is not clearly understood. However, genetics research about hallux valgus is rare. Therefore, the present study aimed to explore the pathogeny of hallux valgus from the perspective of genetics. Human samples were collected from normal bone tissue and hallux valgus region bone tissue. The bone samples were studied using real time-PCR, western blot and immunohistochemical. Lentivirus-mediated miR-182 transfected osteoblasts and tested the expression of FGF9 mRNA with real time-PCR. To test alkaline phosphatase activity, number of calcium nodules and proliferation of osteoblast with enzymatic activity analysis, calcium nodules stained and MTT assay. We found that (1) FGF9 expressed in hallux valgus region bone tissue was significantly higher than normal bone tissue. (2) miR-182 expression levels in hallux valgus region bone tissue were notably lower than those of normal bone tissue. (3) miR-182 could negatively regulate the expression of FGF9 in osteoblasts. (4) FGF9 may enhance osteoblasts proliferation. We have demonstrated that miR-182 promotes the formation of bone by targeting FGF9, implicating an essential role of miR-182 in the etiology of hallux valgus. Moreover, miR-182 might potentially be a therapeutic target for hallux valgus treatment.
Keywords: FGF9; alkaline phosphatase; hallux valgus; miR-182; osteoblast.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Steinberg N, Siev-Ner I, Zeev A. et al. The association between hallux valgus and proximal joint alignment in young female dancers. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(1):67–74. - PubMed
-
- Robinson D, Hasharoni A, Halperin N. et al. Mesenchymal cells and growth factors in bunions. Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20(11):727–732. - PubMed
-
- Soulet L, Chevet E, Lemaitre G. et al. FGFs and their receptors, in vitro and in vivo studies: new FGF receptor in the brain, FGF-1 in muscle, and the use of functional analogues of low-affinity heparin-binding growth factor receptors in tissue repair. Mol Reprod Dev. 1994;39(1):49–55. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara M, Ozono K. Cytokines and osteogenesis. Clin Calcium. 2014;24(6):845–851. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

