Pathogen detection with electrochemical biosensors: Advantages, challenges and future perspectives
- PMID: 33456428
- PMCID: PMC7794054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.114989
Pathogen detection with electrochemical biosensors: Advantages, challenges and future perspectives
Abstract
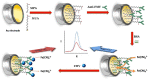
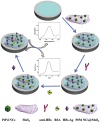
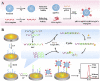
Detection of pathogens, e.g., bacteria and viruses, is still a big challenge in analytical medicine due to their vast number and variety. Developing strategies for rapid, inexpensive, specific, and sensitive detection of the pathogens using nanomaterials, integrating with microfluidics devices, amplification methods, or even combining these strategies have received significant attention. Especially, after the health-threatening COVID-19 outbreak, rapid and sensitive detection of pathogens became very critical. Detection of pathogens could be realized with electrochemical, optical, mass sensitive, or thermal methods. Among them, electrochemical methods are very promising by bringing different advantages, i.e., they exhibit more versatile detection schemes and real-time quantification as well as label-free measurements, which provides a broader application perspective. In this review, we discuss the recent advances for the detection of bacteria and viruses using electrochemical biosensors. Moreover, electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection were broadly reviewed in terms of analyte, bio-recognition and transduction elements. Different fabrication techniques, detection principles, and applications of various pathogens with the electrochemical biosensors were also discussed.
Keywords: Bacteria; Biosensor; Electrochemical biosensor; Electrochemical detection; Pathogen detection; Virus.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Jul 1;159:112214. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112214. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32364936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical biosensors for pathogenic microorganisms detection based on recognition elements.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024 Apr;69(2):283-304. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01144-5. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 38367165 Review.
-
A Critical Review on Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using Electrochemical Biosensors.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2024;52(3):17-40. doi: 10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.2023049469. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38523439 Review.
-
Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Foodborne Bacterial Detection.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2019;49(6):510-533. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2018.1561243. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30648398 Review.
-
Recent Progress in Graphene- and Related Carbon-Nanomaterial-based Electrochemical Biosensors for Early Disease Detection.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022 Mar 14;8(3):964-1000. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00710. Epub 2022 Mar 1. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35229605 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection: An Updated Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;12(11):927. doi: 10.3390/bios12110927. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Early Diagnosis of Viruses Associated with Gastroenteritis by Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 8;12(7):499. doi: 10.3390/bios12070499. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on detection techniques for point-of-care testing of foodborne pathogens.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 8;10:958134. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.958134. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36003541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing Electrochemical Biosensors as an Innovative Platform for the Rapid and On-Site Detection of Animal Viruses.Animals (Basel). 2023 Oct 8;13(19):3141. doi: 10.3390/ani13193141. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective Quantification of Bacteria in Mixtures by Using Glycosylated Polypyrrole/Hydrogel Nanolayers.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Mar 20;16(11):14243-14251. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c14387. Epub 2024 Mar 5. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38442898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- W.H. Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2016. Global Health Estimates 2015: Disease Burden by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2015.
-
- Dietvorst J., Vilaplana L., Uria N., Marco M.-P., Muñoz-Berbel X. Current and near-future technologies for antibiotic susceptibility testing and resistant bacteria detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;127:115891.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
