Stem Cells in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Research Progress of Mechanism
- PMID: 33456473
- PMCID: PMC7785341
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8861251
Stem Cells in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: Research Progress of Mechanism
Abstract
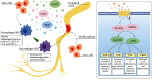
Neuropathic pain (NP) is pain caused by somatosensory nervous system injury or disease. Its prominent symptoms are spontaneous pain, hyperalgesia, and allodynia, and the sense of pain is extremely strong. Owing to the complex mechanism, conventional painkillers lack effectiveness. Recently, research on the treatment of NP by stem cells is increasing and promising results have been achieved in preclinical research. In this review, we briefly introduce the neuropathic pain, the current treatment strategy, and the development of stem cell therapy, and we collected the experimental and clinical trial articles of many kinds of stem cells in the treatment of neuropathic pain from the past ten years. We analyzed and summarized the general efficacy and mechanism of stem cells in the treatment of neuropathic pain. We found that the multiple-mechanism approach was different from the single mechanism of routine clinical drugs; stem cells play a role in peripheral mechanism, central mechanism, and disinhibition of spinal cord level that lead to neuropathic pain, so they are more effective in analgesia and treatment of neuropathic pain.
Copyright © 2020 Meichen Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

