Gandouling Tablets Inhibit Excessive Mitophagy in Toxic Milk (TX) Model Mouse of Wilson Disease via Pink1/Parkin Pathway
- PMID: 33456485
- PMCID: PMC7787754
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3183714
Gandouling Tablets Inhibit Excessive Mitophagy in Toxic Milk (TX) Model Mouse of Wilson Disease via Pink1/Parkin Pathway
Abstract
Objective: Gandouling (GDL) tablet is a Chinese patent medicine approved by the National Medical Product Administration, which is used to treat Wilson disease (WD) in China. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of GDL on mitophagy in the hippocampus in the toxic milk (TX) mouse model of WD.
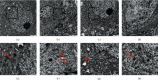
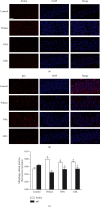
Methods: Mice were randomly divided into the following four groups: control, Wilson (model group), D-penicillamine (DPA), and GDL groups. The animal behaviors were evaluated by the water maze experiment, traction test, and pole test. Transmission electron microscopy was used for the detection of mitochondrion structure. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed for the analysis of the changes in liver function. Colocalization of mitophagy-related proteins was detected by fluorescence microscopy. Western blotting (WB) and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) were conducted for the detection of protein expression and mRNA levels, respectively.
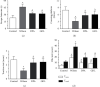
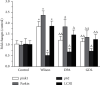
Results: Significant reduction in neurological impairments was observed in the WD model group. All of these results were significantly reversed by GDL intervention. Compared with the levels in the Wilson group, the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), and albumin (ALB) changed obviously. Colocalization between mitophagy-related proteins pink1, parkin, and mitochondria was changed significantly. The mitophagy-related mRNA (pink1, parkin, and LC3II) and protein expression levels (pink1, parkin, and the rate of LC3II/LC3I) were decreased significantly, while p62 was remarkably increased after GDL intervention.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that the neuroprotective mechanism of GDL may occur via the inhibition of excessive mitophagy through the regulation of the pink1/parkin pathway in the TX mouse brain of WD.
Copyright © 2020 Jing Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gandouling Regulates Ferroptosis and Improves Neuroinflammation in Wilson's Disease Through the LCN2/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 23;17:5599-5618. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S465341. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39193124 Free PMC article.
-
[Phosphate and tension homology-induced kinase 1/Parkin signaling mediates cognitive dysfunction in sepsis-associated encephalopathy through activation of hippocampal mitochondrial autophagy].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Apr;35(4):381-386. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220817-00758. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37308193 Chinese.
-
Long-Term Consumption of Food-Derived Chlorogenic Acid Protects Mice against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Promoting PINK1-Dependent Mitophagy and Inhibiting Apoptosis.Toxics. 2022 Nov 5;10(11):665. doi: 10.3390/toxics10110665. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36355956 Free PMC article.
-
Gandouling inhibits hepatic fibrosis in Wilson's disease through Wnt-1/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jul 15;311:116445. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116445. Epub 2023 Apr 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37015279
-
The Role of PTEN-L in Modulating PINK1-Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy.Neurotox Res. 2022 Aug;40(4):1103-1114. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00475-w. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35699891 Review.
Cited by
-
Gandouling Mitigates CuSO4-Induced Heart Injury in Rats.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;12(19):2703. doi: 10.3390/ani12192703. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230444 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of hepatolenticular degeneration research in traditional Chinese medicine using CiteSpace and VOSviewer: A study protocol for systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 6;103(49):e40781. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040781. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39654180 Free PMC article.
-
Gandouling alleviates nerve injury through PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 and Sirt1/FoxO1 signaling pathway to inhibit autophagy in the rats model of Wilson's disease.Brain Behav. 2023 Dec;13(12):e3325. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3325. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 38010098 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Wilson Disease and Its Phenotypes by Using Artificial Intelligence.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):1243. doi: 10.3390/biom11081243. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439909 Free PMC article.
-
Psychiatric Symptoms in Wilson's Disease-Consequence of ATP7B Gene Mutations or Just Coincidence?-Possible Causal Cascades and Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):12354. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212354. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Czlonkowska A., Litwin T. Wilson disease - currently used anticopper therapy. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 2007;142(3):181–191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

