Expression and significance of S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- PMID: 33456516
- PMCID: PMC7791921
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9580
Expression and significance of S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in patients with acute cerebral infarction
Abstract
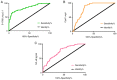
The present study aimed to explore the expression and significance of S100 protein β (S100β), cystatin C (CysC), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in patients with acute cerebral infarction (ACI). ACI patients (n=120) were selected as the experimental group at Xuzhou Central Hospital from August 2016 to August 2018. Ninety healthy subjects who underwent a physical examination at Xuzhou Central Hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. The expression levels of S-100β, CysC and NF-κB were compared between the two groups. Serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB levels were compared between ACI patients with different degree of nervous functional defects, different infarct size and different prognosis. ROC curve analysis was used for the diagnosis of ACI by serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB levels. Serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB levels in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). The levels of serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in patients with different neurological deficits were significantly different. The levels of serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in the severe and medium type infarction group were significantly higher than those in the mild type infarction group (both P<0.05). The levels of serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in the severe type infarction group were higher than those in the medium type infarction group (P<0.05). There were significant differences in serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB levels in patients with different infarct sizes. The levels of serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in patients with large and medium size infarction were higher than those in the small size infarction group (both P<0.05). The levels of serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB in patients with large size infarction were higher than those in patients with medium size infarction (P<0.05). Serum S-100β, CysC and NF-κB levels in patients of the worsening group were significantly higher than those in patients of the non-worsening group. The levels of S-100β, CysC, NF-κB in ACI patients were significantly higher than those in healthy subjects. Increased levels of S-100β, CysC and NF-κB can be used as ideal indexes for diagnosing cerebral infarction and studying the condition.
Keywords: S100 protein β; acute cerebral infarction; cystatin C; diagnose; nuclear factor κB.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated Serum Levels of NSE and S-100β Correlate with Increased Risk of Acute Cerebral Infarction in Asian Populations.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jun 30;21:1879-88. doi: 10.12659/msm.893615. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26124190 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlative study of the metabolic disorder of hippocampus and cerebral cortex and cognitive impairment in moderate to severe OSAHS patients].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;29(7):607-11. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26201184 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Acupuncture Reduces Acute Cerebral Ischemia by Suppressing Local and Peripheral Inflammation and Regulating Expression of Cerebral Protein Silent Information Regulator Factor 2-related Enzyme 1 and Nuclear Factor-κB in Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Mar 25;43(3):146-51. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170372. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 29560629 Chinese.
-
Acute phase serum cathepsin S level and cathepsin S/cystatin C ratio are the associated factors with cerebral infarction and their diagnostic value for cerebral infarction.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 Feb;35(2):95-101. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12014. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30848029 Free PMC article.
-
Role of S-100β in stroke.Int J Neurosci. 2018 Dec;128(12):1180-1187. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2018.1481065. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Int J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29792379 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-124 Is Downregulated in Serum of Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients and Shows Diagnostic and Prognostic Value.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021 Jan-Dec;27:10760296211035446. doi: 10.1177/10760296211035446. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021. PMID: 34702084 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value and mechanism of plasma S100A1 protein in acute ischemic stroke: a prospective and observational study.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 10;11:e14440. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14440. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36643631 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oral ligustrazine phosphate with cerebroside carnosine on neurological function and serum inflammatory factors among patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease: a quasi-experimental study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Mar 10;30(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02414-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40059183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen HJ, He HY, Dai MX. Observation on the therapeutic effect of aspirin in combined with ozagrel sodium in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction. J Hainan Med Univ. 2017;23:141–144. (In Chinese)
-
- Qing-Qing R, Wei-Dong Q, Neurology DO. The role of Th17 in stroke in patients with acute atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. Chin J Stroke, 2017.
-
- Podolecki T, Pudlo R, Mazurek M, Koziel M, Jedrzejczyk-Patej E, Boidol J, Przybylska K, Sokal A, Kowalski O, Kowalczyk J, et al. The incidence, clinical significance, and treatment effects of depression in cardiac resynchronization therapy recipients. Cardiology. 2017;138:115–121. doi: 10.1159/000475522. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Zhou ZF. Correlation analysis of carotid intima media thickness and function in patients with H-type hypertension and acute cerebral infarction. J Hainan Med Univ: 23, 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
