Neutrophils infiltrate into the spiral ligament but not the stria vascularis in the cochlea during lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
- PMID: 33456557
- PMCID: PMC7806478
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.49121
Neutrophils infiltrate into the spiral ligament but not the stria vascularis in the cochlea during lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
Abstract
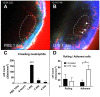
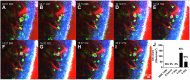
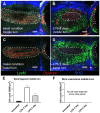
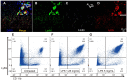
It has been challenging to apply intravital imaging for monitoring the inner ear, as the anatomical location and intricate structure hamper the access of imaging instruments to the inner ear of live mice. By employing intravital imaging of the cochlea in live mice with two-photon microscopy, we investigated neutrophil infiltration into the cochlea tissue and its characteristics under a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory state. Methods: Cochlea inflammation was induced by LPS injection to the middle ear. Using two-photon intravital microscopy with specifically designed surgical exteriorization of the cochlea in live mice, we investigated the dynamic features of neutrophils in the lateral wall of the cochlea. The molecular expression pattern of the cochlea lateral wall was also investigated during the LPS-induce inflammation. Results: Despite the contention of whether neutrophils are recruited to the spiral ligament (SL) during inflammation, we observed that LPS-induced inflammation of the middle ear, which mimics acute otitis media, triggered neutrophil migration to the SL in the lateral wall. Notably, massive neutrophil infiltration to the SL occurred 2 days after LPS inoculation, but there was no neutrophil infiltration into the stria vascularis (SV) region. At 1 day after LPS-induced cochlear inflammation, increased mRNA expression of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 were identified in both the SL and SV, while the ICAM-1 mRNA expression increased only in the SL. The differential reactivity of ICAM-1 is likely responsible for the different neutrophil recruitment pattern in the cochlea. Conclusion: Intravital imaging of the cochlea revealed that neutrophil recruitment and infiltration during inflammation are spatially controlled and exclusively observed in the SL but not in the SV and organ of Corti.
Keywords: cochlea; neutrophil; spiral ligament; stria vascularis; two-photon intravital imaging.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Diaspro A, Robello M. Two-photon excitation of fluorescence for three-dimensional optical imaging of biological structures. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2000;55:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Helmchen F, Denk W. Deep tissue two-photon microscopy. Nat Methods. 2005;2:932–40. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Cho MK, Wu D, Kim HM, Yoon J. Two-Photon Fluorescence Probe for Selective Monitoring of Superoxide in Live Cells and Tissues. Anal Chem. 2019;91:14691–6. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Park SJ, Wu D, Kim HM, Yoon J. A two-photon fluorescent probe for colorimetric and ratiometric monitoring of mercury in live cells and tissues. Chem Commun (Camb) 2019;55:1766–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

