Vitamin D and Immunoglobulin E Status in Allergic Rhinitis Patients Compared to Healthy People
- PMID: 33456593
- PMCID: PMC7803312
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2020-0015
Vitamin D and Immunoglobulin E Status in Allergic Rhinitis Patients Compared to Healthy People
Abstract
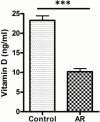
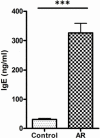
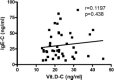
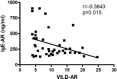
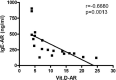
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a type of inflammatory condition that includes a group of symptoms, mainly affecting the nasal mucosa. Nasal obstruction, sneezing, stuffy or runny nose, in addition to swollen, itchy, red and watery eyes are the most common symptoms of the disease. These symptoms are triggered as a result of increased inflammatory mediators such as histamine and leukotrienes. Studies have recently shown the role of vitamin D (vit.D) in many allergic and immune conditions, where receptors for the active form of vit.D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) have been discovered on the surface of almost all types of inflammatory cells. Therefore, the present study was conducted to explore the level of vit. D in AR patients and its correlation with the severity of the disease. Two groups participated in the study; the first group included 49 patients who were diagnosed in a private otolaryngology clinic by the first author as having allergic rhinitis (AR group). The second one served as a control group and included 50 apparently healthy volunteers with no history of AR. The mean level of IgE and vit. D was found to be 326.3 and 10.2 ng/ml in the AR group, respectively, and 30.8 and 23.3 ng/ml in the control group, respectively. Ninety-three percent of AR patients have shown a deficiency in vit. D level, where 56% of this group showed severe deficiency. On the other hand, 34% of the control group has shown an insufficient level of vit. D. Additionally, 64% of AR patients have shown serum levels of IgE at values ranging between 100-299 ng/ml. Higher serum levels of IgE at values ranging between 300-599 ng/ml and 600-1000 ng/ml were observed in 25% and 11% of AR patients, respectively. The prevalence of low levels of vit. D in the AR group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.001). Vit. D deficiency is significantly related to severe AR symptoms and measuring serum vit. D level is recommended in the management plan of this group of patients.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; IgE and allergic rhinitis; vitamin D; vitamin D and IgE; vitamin D and allergic rhinitis.
©Carol Davila University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nasal and Serum Immunoglobulin E Levels in Symptomatic Allergic Rhinitis Patients: A Case-Control Study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Feb;76(1):503-507. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04196-0. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38440571 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between a Deficiency of D3 Levels and the Development of Allergic Rhinitis.Pak J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan;27(1):27-34. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2024.27.34. Pak J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38413395
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels in children with allergic or nonallergic rhinitis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jan;80:39-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26746610
-
Research progress of anti-IGE treatment for allergic rhinitis.Am J Otolaryngol. 2025 May-Jun;46(3):104646. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2025.104646. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Am J Otolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40286545 Review.
-
Anti-IgE treatment in allergic rhinitis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Dec;127:109674. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109674. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31526939 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Interplay between Vitamin D, Insulin Resistance, Obesity and Skeletal Health.J Bone Metab. 2024 May;31(2):75-89. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2024.31.2.75. Epub 2024 May 31. J Bone Metab. 2024. PMID: 38886966 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insight into the Role of Vitamin D in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4798. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104798. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematological, Biochemical, and Serum Levels of Allergic Mediators in Individuals with and without Allergic Rhinitis.J Asthma Allergy. 2024 Jun 4;17:539-549. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S461295. eCollection 2024. J Asthma Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38855057 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers on hematological parameters in type 2 diabetic patients.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;397(3):1817-1828. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02731-y. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37750935
-
V Brazilian Consensus on Rhinitis - 2024.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jan-Feb;91(1):101500. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101500. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39388827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Greiner AN, Hellings PW, Rotiroti G, Scadding GK. Allergic rhinitis. The Lancet. 2011. pp. 2112–22. - PubMed
-
- Sudiro M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is correlated with severity of allergic rhinitis. Open Access Libr J. 2017;4(08):1–9.
-
- Alsamarai AM, Alwan AM, Ahmad AH, Salih MA, Salih JA, Aldabagh MA, et al. The relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis in the Iraqi population. Allergol Int. 2009;58(4):549–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
