The Delivery of Biologically Active Agents into the Nuclei of Target Cells for the Purposes of Translational Medicine
- PMID: 33456977
- PMCID: PMC7800601
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.11049
The Delivery of Biologically Active Agents into the Nuclei of Target Cells for the Purposes of Translational Medicine
Abstract
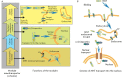
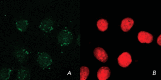
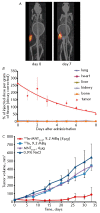
Development of vehicles for the subcellular targeted delivery of biologically active agents is very promising for the purposes of translational medicine. This review summarizes the results obtained by researchers from the Laboratory of Molecular Genetics of Intracellular Transport, Institute of Gene Biology RAS, which allowed them to design the core technology: modular nanotransporters. This approach ensures high efficacy and cell specificity for different anti-cancer agents, as they are delivered into the most vulnerable subcellular compartment within the cells of interest and makes it possible for antibody mimetics to penetrate into a compartment of interest within the target cells ("diving antibodies"). Furthermore, polyplexes, complexes of polycationic block copolymers of DNA, have been developed and characterized. These complexes are efficient both in vitro and in vivo and demonstrate predominant transfection of actively dividing cells.
Keywords: antibody mimetics; drug delivery; gene therapy; modular nanotransporters; photodynamic therapy; polyplexes; radiotherapy.
Copyright ® 2020 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures

References
-
- Sobolev A.S., Herald Russ. Acad. Sci. 2013;83(4):324–335.
-
- Sobolev A.S., Jans D.A., Rosenkranz A.A., Progress Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2000;73(1):51–90. - PubMed
-
- Hall E.J., Giaccia A.J. Radiobiology for the Radiologist. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2019. 1161 p. 2019.
-
- Baade I., Kehlenbach R.H.. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019;58:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Devarajan P.V. Targeted Intracellular Drug Delivery by Receptor Mediated Endocytosis.Cham: Springer, 2019. 560 p. 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
