Genome-wide association study of the TP53 R249S mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma with aflatoxin B1 exposure and infection with hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 33457005
- PMCID: PMC7807280
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-20-510
Genome-wide association study of the TP53 R249S mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma with aflatoxin B1 exposure and infection with hepatitis B virus
Abstract
Background: Exposure to dietary aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) induces DNA damage and mutation in the TP53 gene at codon 249, known as the TP53 R249S mutation, and is a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). AFB1 and the hepatitis B virus (HBV) together exert synergistic effects that promote carcinogenesis and TP53 R249S mutation in HCC.
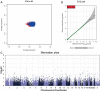
Methods: A genome-wide association study (GWAS) of whole genome exons was conducted using 485 HCC patients with chronic HBV infection. This was followed by an independent replication study conducted using 270 patients with chronic HBV infection. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate TP53 expression in all samples. This showed a correlation between codon 249 mutations and TP53 expression. Susceptibility variants for the TP53 R249S mutation in HCC were identified based on both the GWAS and replication study. The associations between identified variants and the expression levels of their located genes were analyzed in 20 paired independent samples.
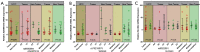
Results: The likelihood of positive TP53 expression was found to be higher in HCC patients with the R249S mutation both in the GWAS (P<0.001) and the replication study (P=0.006). The combined analyses showed that the TP53 R249S mutation was significantly associated with three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): ADAMTS18 rs9930984 (adjusted P=4.84×10-6), WDR49 rs75218075 (adjusted P=7.36×10-5), and SLC8A3 rs8022091 (adjusted P=0.042). The TP53 R249S mutation was found to be highly associated with the TT genotypes of rs9930984 (additive model, P=0.01; dominant model, P=6.43×10-5) and rs75218075 (additive model, P=0.002; dominant model, P=2.16×10-4). Additionally, ADAMTS18 mRNA expression was significantly higher in HCC tissue compared with its expression in paired non-tumor tissue (P=0.041), and patients carrying the TT genotype at rs9930984 showed lower ADAMTS18 expression in non-tumor tissue compared with patients carrying the GT genotype (P=0.0028). WDR49 expression was markedly lower in HCC tissue compared with paired non-tumor tissue (P=0.0011).
Conclusions: TP53 expression is significantly associated with the R249S mutation in HCC. Our collective results suggest that rs9930984, rs75218075, and rs8022091 are associated with R249S mutation susceptibility in HCC patients exposed to AFB1 and HBV infection.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); TP53 mutation; aflatoxin B1 (AFB1); genome-wide association study (GWAS); hepatitis B virus (HBV).
2020 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jgo-20-510). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
