Surgical Approach in Management of Posttraumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia: Thoracotomy versus Laparotomy
- PMID: 33457036
- PMCID: PMC7787844
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6694990
Surgical Approach in Management of Posttraumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia: Thoracotomy versus Laparotomy
Abstract
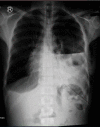
Breach in diaphragmatic musculature permits abdominal viscera to herniate into the thoracic cavity. Time of presentation and associated injuries determines the surgical approach in management. This case report sets to highlight the challenges in clinical diagnosis, radiological interpretation, and surgical management approaches of posttraumatic diaphragmatic hernia. We report a case of a 43 years old male who was diagnosed with traumatic diaphragmatic hernia 6 months post blunt thoracoabdominal trauma due to motor traffic accident. He was initially diagnosed with haemothorax, drained with an underwater thoracostomy tube, and discharged. He continued to experience on and off chest pain worsening postfeeding, difficulty in breathing and abdominal pain for the next six months until his eventual diaphragmatic hernia diagnosis. He was scheduled for an elective thoracotomy. A left posterolateral thoracic over the 7th intercostal space incision was used. Intraoperatively, the stomach, left lobe of liver, part of transverse colon, small bowel, and omentum had herniated into the thoracic cavity adhering into thoracic viscera and wall. Adhesiolysis was done, and abdominal organs reduced into abdominal cavity. Rent was closed by interrupted Prolene sutures reinforced with a mesh. In patients with delayed presentation of diaphragmatic hernia post blunt thoracoabdominal injury without associated intra-abdominal visceral injury, we recommend the thoracic diaphragmatic repair approach as long-standing herniated bowels might adhere with thoracic cavity walls or viscera. In such cases, adhesiolysis and rent repair is easier through thoracotomy.
Copyright © 2020 Ahmed Shabhay et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests. All authors of the manuscript have read and agreed to its contents.
References
-
- Al Kahwa A. Blunt diaphragmatic rupture a case report and literature review. Emergency Medicine: Open Access. 2016;6(4):p. 335. doi: 10.4172/2165-7548.1000335. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources