Effectiveness and safety of nivolumab in the treatment of lung cancer patients in France: preliminary results from the real-world EVIDENS study
- PMID: 33457089
- PMCID: PMC7790497
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1744898
Effectiveness and safety of nivolumab in the treatment of lung cancer patients in France: preliminary results from the real-world EVIDENS study
Abstract
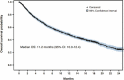
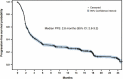
EVIDENS is an ongoing, prospective, non-interventional study evaluating the effectiveness and safety of nivolumab in lung cancer patients in France (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03382496). Adults with a pathologically confirmed diagnosis of lung cancer and initiating treatment with nivolumab were recruited from 146 sites in France. This analysis included only patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who received ≥1 nivolumab infusion, and evaluated patient characteristics at the time of nivolumab initiation and its effectiveness and safety after a median follow-up of 18 months. A total of 1,420 patients with NSCLC were included, most of whom had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) of 0-1 (82.9%), non-squamous histology (69.2%) and stage IV disease (91.4%). Brain metastases were present in 19.9% of patients. Nivolumab was a second-line or ≥third-line regimen in 73.6% and 26.1% of patients, respectively. Almost all patients had prior chemotherapy (99.7%). Median overall survival was 11.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 10.0-12.4). ECOG PS, smoking status, corticosteroids at baseline, epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status, presence of symptomatic brain metastases and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were independent predictors of survival. Grade 3 and 4 TRAEs were reported in 105 (7.4%) and 12 (0.8%) patients, respectively; no treatment-related deaths were reported. Preliminary results of the EVIDENS study confirm the effectiveness and safety of nivolumab, mostly in pre-treated advanced NSCLC patients, with similar benefits to those observed in the phase III randomized clinical trials, despite a broader study population.
Keywords: EVIDENS; france; nivolumab; non-small cell lung cancer; observational study.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute . The essential facts and figures of cancer in France. 2019. [accessed 2019 February26]. http://www.e-cancer.fr/Actualites-et-evenements/Actualites/L-Institut-pu....
-
- Grapatsas K, Leivaditis V, Tsilogianni Z, Haussmann E, Kaplunov V, Dahm M, Zarogoulidis P, Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Tsakiridis K, Foroulis C, et al. Epidemiology, risk factors, symptomatology, TNM classification of non small cell lung cancer. An overview while waiting the 8th TNM classification. Oncomedicine. 2017;2:14–23. doi: 10.7150/oncm.17097. - DOI
-
- Couraud S, Westeel V, Ranchon F, Toffart A-C, Souquet P-J, Editorial board of the 2019 edition. Non-small cell lung cancer. Auvergne Rhône-Alpes guidelines in thoracic oncology. 2019. update 2019 [accessed 2019 May29]. https://ressources-aura.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/CBNPC_2019_VDEF.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials