Sertraline-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- PMID: 33457126
- PMCID: PMC7797414
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12022
Sertraline-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Abstract
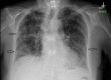
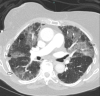
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia (AEP) is a rare but severe respiratory syndrome characterized by fever, hypoxemic respiratory failure, diffuse pulmonary infiltrates, and pulmonary eosinophilia. The most common cause of AEP is idiopathic, but it can be associated with antidepressant medications like sertraline. A 76-year-old female presented to our ED with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. She had no history of smoking or prior lung disease. She did not improve after treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics so a trial of corticosteroids was initiated. Her work-up was negative for infectious or collagen vascular causes of the respiratory failure. She was diagnosed with AEP associated with sertraline. Her condition improved with corticosteroid therapy after discontinuation of sertraline. This case report highlights AEP as a possible adverse reaction of sertraline. Prompt discontinuation of the offending drug is necessary for early recovery.
Keywords: acute eosinophilic pneumonia; antidepressants; eosinophilic pneumonia; sertraline; ssri.
Copyright © 2020, Adhikari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Eosinophilic pneumonia: a review of the previous literature, causes, diagnosis, and management. Suzuki Y, Suda T. Allergol Int. 2019;68:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Eosinophilic lung diseases. Allen JN, Davis WB. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:1423–1438. - PubMed
-
- Acute eosinophilic pneumonia. A summary of 15 cases and review of the literature. Pope-Harman AL, Davis WB, Allen ED, Christoforidis AJ, Allen JN. Medicine. 1996;75:334–342. - PubMed
-
- Pulmonary drug toxicity: radiologic and pathologic manifestations. Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, et al. Radiographics. 2000;20:1245–1259. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources