Inflammation Is Associated with Worse Outcome in the Whole Cohort but with Better Outcome in Triple-Negative Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33457427
- PMCID: PMC7787871
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5618786
Inflammation Is Associated with Worse Outcome in the Whole Cohort but with Better Outcome in Triple-Negative Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
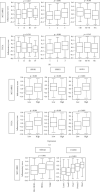
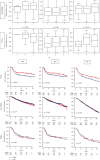
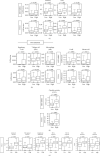
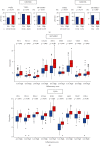
Inflammation has been linked with cancer, but whether it is part of the problem or part of the solution remains to be a matter of debate in breast cancer. Our group and others have demonstrated that inflammation aggravates cancer progression; however, some claim that inflammation may support immune cell infiltration and suppress cancer. We defined the gene set variation analysis of the Molecular Signatures Database Hallmark inflammatory response gene set as the inflammatory pathway score and analyzed 3632 tumors in total from 4 breast cancer cohorts (METABRIC, TCGA, GSE25066, and GSE21094). In the whole breast cancer cohort, high-score tumors were associated with aggressive clinical characteristics, such as worse disease specific survival, higher Nottingham histological grade, and younger age. Inflammatory score was significantly higher in triple-negative (TNBC) as well as basal and normal subtypes compared with the other subtypes, which suggest that the detrimental effect of high level of inflammation may be because it includes a more aggressive subtype. On the contrary, high score within TNBC was significantly associated with better survival. TNBC with high score enriched not only IFN-α, IFN-γ response, IL-2/STAT5 signaling, Allograft rejection, Complement, p53 pathway, Reactive Oxygen, and Apoptosis but also TNF-α signaling, IL6-JAK-STAT signaling, TGF-β signaling, Coagulation, Angiogenesis, EMT, KRAS signaling, and PI3K-AKT-MTOR signaling gene sets. High score was associated with mainly favorable anticancerous immune cell infiltration as well as Leukocyte fraction, TIL regional fraction, Lymphocyte infiltration, IFN-γ response, TGF-β response, and cytolytic activity scores. Although the inflammatory pathway score was not associated with neoadjuvant treatment response, it associated with expressions of immune checkpoint molecules. In conclusion, inflammation was associated with worse outcome in the whole breast cancer cohort, but with better outcome in TNBC, which was associated with favorable anticancerous immune response and immune cell infiltrations.
Copyright © 2020 Masanori Oshi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nauts H. C., Swift W. E., Coley B. L. The treatment of malignant tumors by bacterial toxins as developed by the late William B. Coley, M.D., reviewed in the light of modern research. Cancer Research. 1946;6:205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

