A systematic review and meta-analysis of radiotherapy planning studies comparing multi leaf collimator designs
- PMID: 33458375
- PMCID: PMC7807674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2018.03.005
A systematic review and meta-analysis of radiotherapy planning studies comparing multi leaf collimator designs
Abstract
Background and purpose: Several studies have investigated multi leaf collimator (MLC) leaf design. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of those studies to compare the impact of MLC leaf width used for different radiotherapy techniques.
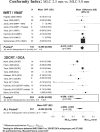
Materials and methods: We decided to focus on 2.5, 3.0 and 5.0 mm leaf width MLCs as it appeared to be the most contentious area from literature. We adopted Cochrane and PRISMA guidelines and computed the association between MLC leaf width and conformity index (CI) across the selected studies as pooled mean difference (PMD) with 95% confidence interval.
Results: A total of 43 papers were selected from the literature search, of which ten compare MLC leaf width of 2.5 mm or 3.0 mm (MLC2.5 mm) versus 5.0 mm (MLC5 mm) in terms of CI. There was a slight, but significant, difference between MLC2.5 mm and MLC5 mm in favor of the former (mean difference -0.036; 95% confidence interval: -0.068 to -0.005). A subgroup analysis was performed by comparing techniques (intensity modulated radiation therapy vs conformal). In the intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) subgroup, the difference between MLC2.5 mm and MLC5 mm appeared to be negligible (mean difference: -0.006; 95% confidence interval: -0.013 to 0.001) and not significantly different from zero. In the subgroup of studies which used conformal techniques, there was a significant difference between MLC2.5 mm and MLC5 mm (mean difference: -0.054; 95% confidence interval: -0.096 to -0.012).
Conclusions: Introduction of IMRT produced comparable target coverage (CI) between 2.5 or 5.0 mm leaf width MLCs.
Keywords: Intensity modulated radiation therapy; Meta-analysis; Multi leaf collimators; Systematic review; Treatment planning system.
© 2018 The Authors.
References
-
- Webb S. Contemporary IMRT: Developing Physics and Clinical Implementation. Series in Med Phys and Biom Eng, Iop.org 2005 ISBN: 0 7503 1004 9 2004.
-
- Wang S-C, Wang X, Yin-Bo H, Zhao Y-Q, Tao L, Ping A, et al. A dosimetric comparison of the fixed-beam IMRT plans using different leaf width of multileaf collimators for the intermediate risk prostate cancer. Rad Phys Chem n.d. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.07.008.
-
- Fujimoto S., Ono K., Furukawa K., Kudo T., Akagi Y., Koyama T. Influence of high-definition multileaf collimator for three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2012;68:825–834. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources