Dopamine induces functional extracellular traps in microglia
- PMID: 33458617
- PMCID: PMC7797945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101968
Dopamine induces functional extracellular traps in microglia
Abstract
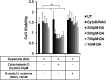
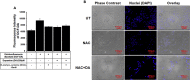
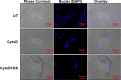
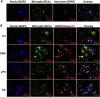
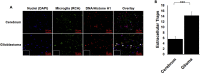
Dopamine (DA) plays many roles in the brain, especially in movement, motivation, and reinforcement of behavior; however, its role in regulating innate immunity is not clear. Here, we show that DA can induce DNA-based extracellular traps in primary, adult, human microglia and BV2 microglia cell line. These DNA-based extracellular traps are formed independent of reactive oxygen species, actin polymerization, and cell death. These traps are functional and capture fluorescein (FITC)-tagged Escherichia coli even when reactive oxygen species production or actin polymerization is inhibited. We show that microglial extracellular traps are present in Glioblastoma multiforme. This is crucial because Glioblastoma multiforme cells are known to secrete DA. Our findings demonstrate that DA plays a significant role in sterile neuro-inflammation by inducing microglia extracellular traps.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Cellular Neuroscience; Immunology; Molecular Biology.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Agrawal I., Saxena S., Nair P., Jha D., Jha S. Obtaining Human Microglia from Adult Human Brain Tissue. JoVE. 2020;162:e61438. - PubMed
-
- Basu S., Nagy J.A., Pal S., Vasile E., Eckelhoefer I.A., Susan Bliss V., Manseau E.J., Dasgupta P.S., Dvorak H.F., Mukhopadhyay D. The neurotransmitter dopamine inhibits angiogenesis induced by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat. Med. 2001;7:569–574. - PubMed
-
- Beninger R.J. The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res. 1983;287:173–196. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

