WIDOCK: a reactive docking protocol for virtual screening of covalent inhibitors
- PMID: 33458809
- PMCID: PMC7904743
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-020-00371-5
WIDOCK: a reactive docking protocol for virtual screening of covalent inhibitors
Abstract
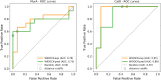
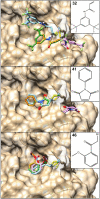
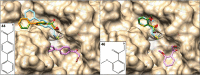
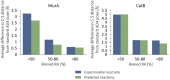
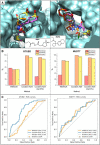
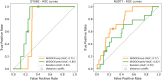
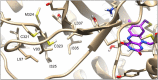
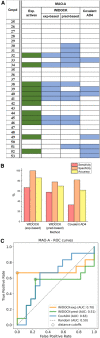
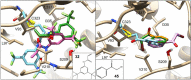
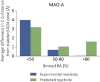
Here we present WIDOCK, a virtual screening protocol that supports the selection of diverse electrophiles as covalent inhibitors by incorporating ligand reactivity towards cysteine residues into AutoDock4. WIDOCK applies the reactive docking method (Backus et al. in Nature 534:570-574, 2016) and extends it into a virtual screening tool by introducing facile experimental or computational parametrization and a ligand focused evaluation scheme together with a retrospective and prospective validation against various therapeutically relevant targets. Parameters accounting for ligand reactivity are derived from experimental reaction kinetic data or alternatively from computed reaction barriers. The performance of this docking protocol was first evaluated by investigating compound series with diverse warhead chemotypes against KRASG12C, MurA and cathepsin B. In addition, WIDOCK was challenged on larger electrophilic libraries screened against OTUB2 and NUDT7. These retrospective analyses showed high sensitivity in retrieving experimental actives, by also leading to superior ROC curves, AUC values and better enrichments than the standard covalent docking tool available in AutoDock4 when compound collections with diverse warheads were investigated. Finally, we applied WIDOCK for the prospective identification of covalent human MAO-A inhibitors acting via a new mechanism by binding to Cys323. The inhibitory activity of several predicted compounds was experimentally confirmed and the labelling of Cys323 was proved by subsequent MS/MS measurements. These findings demonstrate the usefulness of WIDOCK as a warhead-sensitive, covalent virtual screening protocol.
Keywords: Covalent docking; Covalent inhibitors; Virtual screening; Warhead reactivity.
Figures

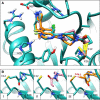
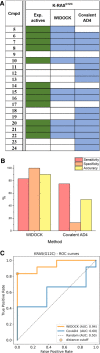
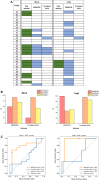
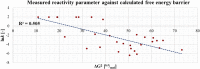
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

