Risk of overanticoagulation during acute kidney injury in patients treated with vitamin K antagonists
- PMID: 33459792
- PMCID: PMC8951229
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfab008
Risk of overanticoagulation during acute kidney injury in patients treated with vitamin K antagonists
Abstract
Background: Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) are still in use for oral anticoagulation, but not all indications allow their replacement by direct oral anticoagulants. Although formal dose reduction is not required in patients with impaired kidney function, case reports indicate that acute kidney injury (AKI) might be associated with derailment of VKA therapy.
Methods: The study retrospectively collected patients from a tertiary nephrology care centre who experienced AKI while being treated with VKA. In these individuals, the international normalized ratio (INR) as a measure of anticoagulant effect during renal failure was compared with a reference time point with stable kidney function.
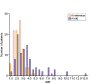
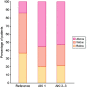
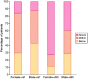
Results: A total of 100 patients with AKI and ongoing VKA therapy met the inclusion criteria. The majority (76%) of patients had AKI with CKD. Volume depletion (n = 43), septic renal failure (n = 22), decompensated heart failure (n = 18) and toxic renal damage (n = 11) were the most important causes of AKI. The average INR values at the time of AKI were higher than at the reference time point [median 3.17 (range 1.10-13.0) versus 2.24 (1.07-5.17); P < 0.0001]. Fifty-four patients had INR values above the recommended therapeutic range for their indication at the time point of AKI. Bleeding complications occurred in 24 patients during AKI and the VKA dose had to be reduced in 55. Women, patients with low body mass index and patients with diabetes were predisposed to overanticoagulation during AKI.
Conclusions: The effect of AKI on anticoagulation by VKA has not been systematically described. This risk should be considered in patients at high risk for AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; anticoagulant therapy; bleeding; chronic kidney disease; drug interactions.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures

References
-
- Dahal K, Kunwar S, Rijal Jet al.. Stroke, major bleeding, and mortality outcomes in warfarin users with atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Chest 2016; 149: 951–959 - PubMed
-
- Arnason B, Matthisson J, Madsen H. [Can acute renal insufficiency increase the effect of warfarin?]. Ugeskr Laeger 2009; 171: 1012 - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2012; 2:8
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

