CaMKII-dependent ryanodine receptor phosphorylation mediates sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 33460250
- PMCID: PMC7520277
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15470
CaMKII-dependent ryanodine receptor phosphorylation mediates sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
Abstract
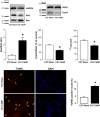
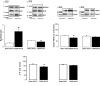
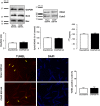
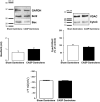
Sepsis is associated with cardiac dysfunction, which is at least in part due to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. However, the underlying mechanisms are far from being understood. Using the colon ascendens stent peritonitis mouse model of sepsis (CASP), we examined the subcellular mechanisms that mediate sepsis-induced apoptosis. Wild-type (WT) CASP mice hearts showed an increase in apoptosis respect to WT-Sham. CASP transgenic mice expressing a CaMKII inhibitory peptide (AC3-I) were protected against sepsis-induced apoptosis. Dantrolene, used to reduce ryanodine receptor (RyR) diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release, prevented apoptosis in WT-CASP. To examine whether CaMKII-dependent RyR2 phosphorylation mediates diastolic Ca2+ release and apoptosis in sepsis, we evaluated apoptosis in mutant mice hearts that have the CaMKII phosphorylation site of RyR2 (Serine 2814) mutated to Alanine (S2814A). S2814A CASP mice did not show increased apoptosis. Consistent with RyR2 phosphorylation-dependent enhancement in diastolic SR Ca2+ release leading to mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, mitochondrial Ca2+ retention capacity was reduced in mitochondria isolated from WT-CASP compared to Sham and this reduction was absent in mitochondria from CASP S2814A or dantrolene-treated mice. We conclude that in sepsis, CaMKII-dependent RyR2 phosphorylation results in diastolic Ca2+ release from SR which leads to mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and apoptosis.
Keywords: CaMKII; Sepsis; apoptosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; ryanodine receptors.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium/Calmodulin Protein Kinase II-Dependent Ryanodine Receptor Phosphorylation Mediates Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction Associated With Sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2017 Apr;45(4):e399-e408. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002101. Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 27648519
-
Calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates the intracellular signalling pathways of cardiac apoptosis in mice with impaired glucose tolerance.J Physiol. 2017 Jun 15;595(12):4089-4108. doi: 10.1113/JP273714. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28105734 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase IIδC-induced chronic heart failure does not depend on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Aug;11(4):2191-2199. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14772. Epub 2024 Apr 14. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38616546 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac ryanodine receptor phosphorylation by CaM Kinase II: keeping the balance right.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jun 1;14(13):5134-56. doi: 10.2741/3591. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482609 Review.
-
Muscarinic Stimulation Facilitates Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca Release by Modulating Ryanodine Receptor 2 Phosphorylation Through Protein Kinase G and Ca/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II.Hypertension. 2016 Nov;68(5):1171-1178. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07666. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27647848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CaMKII may regulate renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis through YAP/NFAT2 in acute kidney injury mice.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2172961. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2172961. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 36718671 Free PMC article.
-
IL-13 Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis by Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mitochondria.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 17;9:736603. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736603. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604237 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial calcification: case reports and a systematic review.Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2024 Jul 30;2(3):qyae079. doi: 10.1093/ehjimp/qyae079. eCollection 2024 Jul. Eur Heart J Imaging Methods Pract. 2024. PMID: 39224618 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: mitochondria and energy metabolism.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025 Feb 18;13(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40635-025-00728-w. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025. PMID: 39966268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RCAN1 deficiency aggravates sepsis-induced cardiac remodeling and dysfunction by accelerating mitochondrial pathological fission.Inflamm Res. 2022 Dec;71(12):1589-1602. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01628-5. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36305917
References
-
- Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K, Treggiari MM. Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: an ongoing challenge. Shock. 2014;41:12‐24. - PubMed
-
- Merx MW, Weber C. Sepsis and the heart. Circulation. 2007;116:793‐802. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A, Aberle NS, Ren J, Sharma AC. Endothelin‐converting enzyme‐1‐mediated signaling in adult rat ventricular myocyte contractility and apoptosis during sepsis. J Moll Cell Cardiol. 2005;38(3):527‐537. - PubMed
-
- Lancel S, Joulin O, Favory R, et al. Neviere R: Ventricular myocyte caspases are directly responsible for endotoxin‐induced cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 2005;24:111(20): 2596–604. - PubMed
-
- Baranek JT. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis contributes to the pathology of the septic shock heart. Intesive Care Med. 2002;28(2):218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

