(3α,5α)3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) regulation of hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic corticotropin releasing factor (CRF): Sexual dimorphism and brain region specificity in Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 33460689
- PMCID: PMC8010646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108463
(3α,5α)3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) regulation of hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic corticotropin releasing factor (CRF): Sexual dimorphism and brain region specificity in Sprague Dawley rats
Abstract
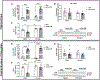
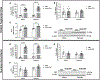
CRF is the main activator of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in response to stress. CRF neurons are found mainly in the hypothalamus, but CRF positive cells and CRF1 receptors are also found in extrahypothalamic structures, including amygdala (CeA), hippocampus, NAc and VTA. CRF release in the hypothalamus is regulated by inhibitory GABAergic interneurons and extrahypothalamic glutamatergic inputs, and disruption of this balance is found in stress-related disorders and addiction. (3α,5α)3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP), the most potent positive modulator of GABAA receptors, attenuates the stress response reducing hypothalamic CRF mRNA expression and ACTH and corticosterone serum levels. In this study, we explored 3α,5α-THP regulation of hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic CRF mRNA and peptide expression, in male and female Sprague Dawley rats, following vehicle or 3α,5α-THP administration (15 mg/kg). In the hypothalamus, we found sex differences in CRF mRNA expression (females +74%, p < 0.01) and CRF peptide levels (females -71%, p < 0.001). 3α,5α-THP administration reduced hypothalamic CRF mRNA expression only in males (-50%, p < 0.05) and did not alter CRF peptide expression in either sex. In hippocampus and CeA, 3α,5α-THP administration reduced CRF peptide concentrations only in the male (hippocampus -29%, p < 0.05; CeA -62%, p < 0.01). In contrast, 3α,5α-THP injection increased CRF peptide concentration in the VTA of both males (+32%, p < 0.01) and females (+26%, p < 0.01). The results show sex and region-specific regulation of CRF signals and the response to 3α,5α-THP administration. This data may be key to successful development of therapeutic approaches for stress-related disorders and addiction.
Keywords: 3α,5α-THP; CRF; Extrahypothalamic CRF; HPA axis; Sex differences.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

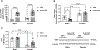
References
-
- Akhter N, Madhoun A, Arefanian H, Wilson A, Kochumon S, Thomas R, Shenouda S, Al-Mulla F, Ahmad R, Sindhu S, 2019. Oxidative stress induces expression of the toll-like receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4 in the human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for metabolic inflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem 53 (1), 1–18. 10.33594/000000117. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

