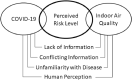
Indoor air quality and COVID-19
- PMID: 33460881
- PMCID: PMC7203025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.04.047
Indoor air quality and COVID-19
Figures
Comment on
-
Aerosol and Surface Stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared with SARS-CoV-1.N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 16;382(16):1564-1567. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004973. Epub 2020 Mar 17. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32182409 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tham K. Indoor air quality and its effects on humans – a review of challenges and developments in the last 30 years. Energy Build. 2016;130:637–650.
-
- Yu I., Li Y., Wong T., Tam W., Chan A., Lee J., Leung D., Ho T. Evidence of airborne transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1731–1739. - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Leung G., Tang J., Yang X., Chao C., Lin J., Lu J., Nielsen P., Niu J., Qian H., Sleigh A., Su H., Sundell J., Wong T., Yuen P. Role of ventilation in airborne transmission of infectious agents in the built environment – a multidisciplinary systematic review. Indoor Air. 2007;17:2–18. - PubMed
-
- Weschler C. Changes in indoor pollutants since the 1950. Atmos Environ. 2009;43:153–169.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical